Day
|
Years ago
|
Period (approx.)/Entity(ies) created
|
1
|
12,000-11,000
|
10,000-9000
B.C.; light
|
2
|
11,000-10,000
|
9000-8000
B.C.; firmament, waters above/below
|
3
|
10,000-9,000
|
8000-7000
B.C.; grass, herbs, trees
|
4
|
9,000-8,000
|
7000-6000
B.C.; sun, moon, stars
|
5
|
8,000-7,000
|
6000-5000
B.C.; sea creatures, flying creatures
|
6
|
7,000-6,000
|
5000-4000
B.C.; land animals, creeping things, man
|
7
|
6,000-5,000
|
4000-3000
B.C. (God’s day of rest)
|
8
|
5,000-4,000
|
3000-2000
B.C.
|
9
|
4,000-3,000
|
2000-1000
B.C.
|
10
|
3,000-2,000
|
1000-1
B.C.
|
11
|
2,000-1,000
|
1-1000
A.D.
|
12
|
1,000-recent
|
1000-2000
A.D.
|
Total: 12,000
|
||
13
|
Present-
|
2000-3000
A.D. (man’s Millennium rest)
|
14
|
3000-4000
A.D. (God’s next day of rest)
|
Day
|
Start b.p.*
|
Duration
|
End b.p.
|
Bible
|
Science
|
1
|
15¾billion
|
8 billion
|
7¾billion
|
Light
|
Big Bang, light, electrons, atoms, galaxies
|
2
|
7 ¾ billion
|
4 billion
|
3¾billion
|
Firmament
|
Milky Way, Sun
|
3
|
3 ¾ billion
|
2 billion
|
1¾billion
|
Oceans, dry land, plants
|
Earth cooled, bodies of water, bacteria, algae
|
4
|
1 ¾ billion
|
1 billion
|
¾ billion
|
Sun, moon, stars
|
Clear, oxygen-rich atmosphere
|
5
|
¾ billion
|
½billion
|
¼ billion
|
Aquatic animals, reptiles, winged animals
|
Multi-cellular, aquatic animals, winged insects
|
6
|
¼ billion
|
¼ billion
|
ca. 6,000
|
Land animals, mammals, humankind
|
90% extinction, hominids, humans
|
15¾billion
|
Day
|
First Triad: “Realms”
|
Second Triad: “Rulers”
|
Day
|
1
|
Darkness and light, night and day
|
Sun, moon, and stars –
to rule the day and the night
|
4
|
2
|
The firmament,
waters under and above
|
Creatures in the waters,
fowl that fly in the firmament
|
5
|
3
|
Waters and dry land; grass, herbs, trees
|
Beasts of the earth, cattle, creeping things, man
|
6
|
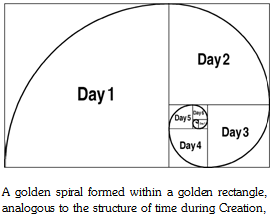
The scenarios of Creation events appeared smaller and smaller in scope with each new “day.” Time seems to have advanced on a similarly decreasing scale during Creation “week.” It has been likened to a spiral, a frequently occurring figure in nature, to demonstrate the diminishing rate. An exponential spiral can be graphically derived from and illustrated in a golden rectangle.
Day-Age
|
Length in Yrs.
|
Start, Yrs. Ago
|
End, Yrs. Ago
|
1
|
7,500,000,000
|
15,000,000,000
|
7,500,000,000
|
2
|
3,750,000,000
|
7,500,000,000
|
3,750,000,000
|
3
|
1,875,000,000
|
3,750,000,000
|
1,875,000,000
|
4
|
937,500,000
|
1,875,000,000
|
937,500,000
|
5
|
468,750,000
|
937,500,000
|
468,750,000
|
6**
|
234,375,000
|
468,750,000
|
234,375,000
|
(7)
|
117,187,500
|
234,375,000
|
117,187,500
|
(1)
|
58,593,750
|
117,187,500
|
58,593,750
|
(2)
|
29,296,875
|
58,593,750
|
29,296,875
|
(3)
|
14,648,438
|
29,296,875
|
14,648,438
|
(4)
|
7,324,219
|
14,648,438
|
7,324,219
|
(5)
|
3,662,110
|
7,324,219
|
3,662,110
|
(6)
|
1,831,055
|
3,662,110
|
1,831,055
|
(7)
|
915,528
|
1,831,055
|
915,528
|
(1)
|
457,764
|
915,528
|
457,764
|
(2)
|
228,882
|
457,764
|
228,882
|
(3)
|
114,441
|
228,882
|
114,441
|
(4)
|
57,221
|
114,441
|
57,221
|
(5)
|
28,611
|
57,221
|
28,611
|
(6)
|
14,306
|
28,611
|
14,306
|
Sub-total:
|
14,999,992,847
| ||
7
|
7,153
|
14,306
|
7,153
|
4000 B.C.-3000 A.D.
|
~6,000
|
on-going
| |
Total:
|
15,000,000,000
|
- Literal 24-Hour Days: 5 days before man was created circa 6,000 years ago
- Thousand-Year Days: circa 12,000-11,000 years ago
- Diminishing Day-Ages: circa 15,000,000,000-7,500,000,000 years ago (Duration: approximately 7,500,000,000 years)
- Literal 24-Hour Days: 4
days before man was created circa 6,000 years ago
- Thousand-Year Days:
circa 11,000-10,000 years ago
- Diminishing Day-Ages: circa 7,500,000,000-3,750,000,000 years ago (Duration: approximately 3,750,000,000 years)
Primordial Planet Puzzles (Part 3)
Day
3: Seas, dry land, vegetation
“And God said, Let the waters under the heaven be gathered together unto one place, and let the dry land appear: and it was so. And God called the dry land Earth; and the gathering together of the waters called he Seas: and God saw that it was good” (Gen 1:9-13).
Interpretations
of Day 3:
- Literal 24-Hour Days: 3
days before man was created circa 6,000 years ago
- Thousand-Year Days:
circa 10,000-9,000 years ago
- Diminishing Day-Ages: circa 3,750,000,000-1,875,000,000 years
ago (Duration: approximately 1,875,000,000 years)
Young
Earth Creationists say God separated the seas and the dry land either around
6,000 years ago or 10,000-9,000 years ago.
In the Diminishing Day-Ages chronology,
God gathered the seas for the dry land to appear between 3.75 billion and 1.875
billion years ago. The scientific estimate for the appearance of the oceans
falls exactly within this period. The Encyclopaedia
Britannica says that “the oceans have been present for at least three
billion years.”29
One supercontinent.
As
the waters came together, the exposed dry surface of the planet became one vast
supercontinent surrounded by an immense ocean.
Scientists
confirmed the Scriptures early in the 20th century. German
geophysicist Alfred Wegener, intrigued by the matching contours of the
coastlines of eastern
Canadian geologist John Tuzo Wilson posits that the continents
have been repeatedly breaking up and rejoining (“
The
plant kingdom
“And God said, Let the earth bring
forth grass, the herb yielding seed, and the fruit tree yielding fruit after
his kind, whose seed is in itself, upon the earth: and it was so. And the earth
brought forth grass, and herb yielding seed after his kind, and the tree
yielding fruit, whose seed was in itself, after his kind: and God saw that it
was good. And the evening and the morning were the third day” (Gen 1:9-13).
God
created the first living things on Earth – plants – on Day 3. The World
Book says the oldest fossils are those of bacteria that lived about 3.5
billion years ago.31 Paleobiologists say these organisms
(microscopic plants) appeared as soon as there was water on Earth. The timing
is again a perfect match, because Day 3 in the Diminishing Day-Ages was from
3.75 billion to 1.875 billion years ago.
Cells to grass to trees.
The
bacteria were one-celled prokaryotes (no nuclei). Cyanobacteria (blue-green
algae) with chlorophyll were capable of photosynthesis. They were followed by
unicellular organisms with nuclei (eukaryotes); then multi-celled vegetation
like moss, grass, herbs, trees.
The
Jewish sage Nachmanides said the creation of grasses, plants, and trees
actually transpired over a protracted period.32 The Genesis writer
simply had the tendency to summarize a string of events in one or two
sentences, rather than make a long-winded, detailed narration. After all, even
if he did lengthily describe a bacterium that could not be seen by the unaided
eye, would he have been understood and, more importantly, believed by his
fellow desert nomads 3,500 years ago?
Prefab components?
God said, “Let the earth bring forth…” The wording implies that the elements
that would constitute the grass, herbs, and trees had been laid down in the
earth earlier. The various “prefabricated” components were just waiting to
combine into specific forms at God’s command.
Note that each type of plant life
reproduced “after his kind,” showing
that the Creator had set the fixed laws of genetics in operation.
Plants without a sun?
At
this point, there was still no mention of the sun. How did the first plants
manage to survive without sunlight for photosynthesis? We get the answer from
prophecy. In Acts
We
are told that in the future
Day 4: Sun, moon, and
stars
“And
God said, Let there be lights in the firmament of the heaven to divide the day
from the night; and let them be for signs, and for seasons, and for days, and
years: And let them be for lights in the firmament of the heaven to give light
upon the earth: and it was so. And God made two great lights; the greater light
to rule the day, and the lesser light to rule the night: he made the stars
also. And God set them in the firmament of the heaven to give light upon the
earth, And to rule over the day and over the night, and to divide the light
from the darkness: and God saw that it was good. And the evening and the
morning were the fourth day” (Gen
Interpretations
of Day 4:
- Literal 24-hour Days:
2 days before man was created 6,000 circa years ago
- Thousand-Year Days:
circa 9,000-8,000 years ago
- Diminishing Day-Ages: circa 1,875,000,000-937,500,000 years
ago (Duration: approximately 937,500,000 years)
Young
Earth Creationists hold that the sun, moon, stars, and other heavenly bodies
were created either just 6,000 years ago or 9,000-8,000 years ago at the most.
In
the Diminishing Day-Ages, the celestial lights first shone on Earth sometime
between 1.875 billion and 937.5 million years ago (mya).
“Made”
or “had made”?
The
Creator used the words “let there be” and
“let them be,” which could mean that
the heavenly bodies were already in existence before Day 4. In the phrase “And God made…” the word translated “made” is from the Hebrew asah, (“to do or make”), which can be translated
into several words in English, but “to create” is not one of them.
The
verb form in English is in the simple past tense (“made”). However, the
pluperfect or past perfect tense “had
made,” indicating a prior act, could
have also been used to translate asah
(ex.: Gen 1:31, 2:2, 3:1, etc.). Hence, the verse could also be rendered as: “And God had made two great lights…” Gen
1:16a), implying God had earlier created the sun, moon, and stars before they
became visible on earth.
Gas
clouds thinned?
Possibly,
after the Earth had formed, the lighter gases which did not become part of the
solid sphere continued to surround the planet – the way some planets, like
Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, are still
shrouded with gas clouds today. Venus is covered by a gaseous canopy so thick
that astronomers cannot see its surface. Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, is also
veiled by a thick blur of gases.
The
Earth’s cloudy atmosphere could have thinned and become clear sometime between
1,875,000,000 and 937,000,000 years ago. From a viewpoint on the surface of the
planet, that would have been the first time the sun, moon, and stars shone from
the sky.
Moreover, according to ScienceDaily, “The
primitive sun did not use to shine as brightly as it does at present. Four billion
years ago the solar output was only about 60% of what it is today.”33
The weak rays of the young sun would not have been able to
penetrate Earth’s dense gaseous atmosphere, which might have been merely
translucent.
Signs
in the stars.
The
Bible says God arranged the celestial bodies in certain ways for particular
reasons: “And God said, Let there be
lights in the firmament of the heaven to divide the day from the night; and let
them be for signs…” (Gen 1:14, cf. Dan 6:27).
The
sun, moon, stars, and other celestial objects bear messages from God! “The heavens declare the glory of God; and
the firmament sheweth his handywork. Day unto day uttereth speech, and night
unto night sheweth knowledge. There is no speech nor language, where their
voice is not heard. Their line is gone out through all the earth, and their
words to the end of the world…” (Ps 19:1-4a). To communicate His messages,
God uses a heavenly language that can be understood by all peoples.
The Mazzaroth.
Men in
The
constellations seem to have been named at the time of the Tower of Babel37
circa 2000 B.C., and arranged in groups around 700 B.C.38 The
earliest known zodiac with all 12 signs dates from the 400s B.C.39
At least one fragment of the Dead Sea Scrolls, from the 200s B.C., lists the
signs of the Zodiac.40 Adopting the Babylonian symbols that mostly represent
animals, the Greeks called them ta zōdia,
“the little animals,” or zōdiakos kyklos (“circle of animals”).41
The Egyptians and the Chinese also used the 12 divisions, but gave other names
and symbols to them.42
The Magi. Some Biblical personages appear to have
been astrologers: “And the king communed
with them; and among them all was found none like Daniel, Hananiah, Mishael,
and Azariah: therefore stood they before the king. And in all matters of wisdom
and understanding, that the king inquired of them, he found them ten times
better than all the magicians and astrologers that were in all his realm” (Dan
1:19-20).
Daniel
was made the king’s top astrologer: “There
is a man in your kingdom who has the spirit of the holy gods in him. In the
time of your father he was found to have insight and intelligence and wisdom
like that of the gods. King Nebuchadnezzar your father -- your father the king,
I say -- appointed him chief of the magicians, enchanters, astrologers and
diviners” (Dan
Daniel
probably passed on his knowledge to his assistants, especially fellow-Jews in
Starry
story.
First
century Jewish historian Flavius Josephus wrote of an ancient belief that
Adam’s son Seth and great-great grandson Enoch saw a drama inscribed in the
starlit night sky. The starry story is said to be the salvation of man by a
coming Messiah. How do we read the story? Where does it start? The
constellations in the celestial circle have no apparent beginning or end.
Ancient astrologers started the year from Aries, where the sun was at the
spring equinox. Should we do likewise?
Egyptologist
Frances Rolleston found the key in the 4,000-year-old zodiac of Dendereh on the
ceiling of the portico of the
Gospel in the stars. Interpretations of the 12
constellations slightly vary, but the overall picture they paint is the same:
the Gospel is in the stars! Below is a synthesis of the basic meaning of each
sign:
1. Virgo, the Virgin: a sinless woman (the
pure faith, church, or religion) carrying an infant and holding a branch (the
Messiah);
2. Libra, the Weighing Scales: purchase
and judgment -- the son of the woman will pay the price (for sin) and act as
the coming judge;
3. Scorpio, the Scorpion (formerly the
snake Serpens battling the eagle
4. Sagittarius, the Archer or mighty
hunter: the Antichrist defying God and attempting to kill His Only Son, the
Savior of mankind;
5. Capricorn, the Goat-Fish or wounded
scapegoat: the sacrificial offering was pierced (His blood as atonement for the
sins of the world);
6. Aquarius, the Water-Bearer: God pouring
His Holy Spirit (water) upon the earth, baptizing the body of believers during
the Church Age;
7. Pisces, the Fishes (a small one and a
big one): the Judeo-Christian faith, made up of two groups of people who will
be saved;
8. Aries, the Ram: the sacrificed Lamb of
God, the Messiah, who has grown greater
and more powerful through His death on the cross;
9. Taurus, the Bull: the power and
longsuffering of God, patiently waiting for men to repent of their sins before
rendering judgment;
10. Gemini, the Twins: two children of the
same woman (faith), also symbolic of the Bridegroom (the Messiah) and His bride
(the Church);
11. Cancer, the Crab (formerly a
sheepfold): the ingathering of the flock at the “Rapture” or first resurrection
at Christ’s Second Coming;
12. Leo, the Lion: the return of Christ as
Lion of Judah, pouncing on the serpent Hydra (Satan) stretching over a third of
the stars (angels).
Do
you see the complete story?
Horoscopes? Horrors!
The Mazzaroth
reveals God’s plan for His chosen people. But Gentile stargazers began making predictions
for their countrymen – such as national prosperity or disaster. (“Dis-aster”
comes from the Latin words dis [“reverse”)
and aster [“star”], a reversal or
disarrangement of the stars.) The Greeks and Romans started casting personal horoscopes
sometime between 600 and 200 B.C.44 Fortune-telling, however,
including horoscopes, is detestable to God: “There shall not be found among you any one that maketh his son or his
daughter to pass through the fire, or that useth divination, or an observer of
times, or an enchanter, or a witch, Or a charmer, or a consulter with familiar
spirits, or a wizard, or a necromancer. For all that do these things are an
abomination unto the LORD” (Deut
Jeremiah
told the Jews: “Thus says the LORD:
"Do not learn the way of the Gentiles; Do not be dismayed at the signs of
heaven, For the Gentiles are dismayed at them. For the customs of the peoples
are futile…” (Jer 10:2-3a, NKJV).
____________________
34Astronomy, International Standard Bible Encyclopaedia
43F. Chris Patrick, The Zodiac Conspiracy, 1993, p. 13
(Excerpted from Chapter 4, Primordial Planet Puzzles, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Primordial Planet Puzzles (Part 4)
Day 5: Water creatures, fowl
“And God said, Let the waters bring forth abundantly the moving creature that hath life, and fowl that may fly above the earth in the open firmament of heaven. And God created great whales, and every living creature that moveth, which the waters brought forth abundantly, after their kind, and every winged fowl after his kind: and God saw that it was good. And God blessed them, saying, Be fruitful, and multiply, and fill the waters in the seas, and let fowl multiply in the earth. And the evening and the morning were the fifth day” (Gen
Interpretations of Day 5:
- Literal 24-Hour Days: 1 day before man was created circa 6,000 years ago
- Thousand-Year Days: circa 8,000-7,000 years ago
- Diminishing Day-Ages: circa 937,500,000-468,750,000 years ago (Duration: approximately 468,750,000 years)
According to Young Earth Creationists, aquatic creatures and birds first appeared no later than 6,000 years ago, but no earlier than 8,000-7,000 years ago, either.
In the Diminishing Day-Ages timeline, God created the first marine animals during Day-Age 5, sometime between 937.5 million and 468.75 million years ago. This corresponds precisely to the oldest known animal fossils, about 700 million years old, that the Encyclopedia Britannica identifies as Ediacara fauna, small wormlike creatures with soft bodies.45
Oxygen-breathing animals.
Until about 700 million years ago, there was a negligibly low amount of oxygen available. (The estimated threshold or minimum amount of oxygen needed for animal life to begin and multiply on earth is 1-10% of the present atmospheric level.)46 Photosynthesizing bacteria then began oxygenating the oceans to produce the oxygen needed by new marine animals that derived energy through respiration.
Do you see the thoughtful planning involved? God created plants on Day 3 to produce oxygen. After an adequate supply had been assured, He proceeded to create oxygen-breathing animals on Day 5.
The Cambrian “explosion.”
Approximately 544 million years ago, new forms of life with various anatomical structures appeared in rapid succession.47 Writer Leslie Orgel said in the New Scientist: “Beginning at the base of the Cambrian period and extending for about 10 million years, all the major groups of skeletonized invertebrates made their first appearance in the most spectacular rise in diversity ever recorded on our planet.”48
All the basic shapes and features of multi-cellular organisms living today first appeared during that period: mouths, eyes, gills, intestines, shells, bones, spines, appendages, joints. The seas teemed with a great variety of invertebrates: sponges, worms, bryozoans (“moss animals”), hydrozoans (jellyfish), brachiopods (clams), mollusks (snails), arthropods (trilobites), echinoderms (starfish).49
Sir Jonathan Sacks wonders, “Something’ happened to cause an ‘explosion’ of complex multi-cellular body forms. Scientists have long been puzzled about why this burst of diversity occurred… How did life evolve at such speed that even Francis Crick, co-discoverer of DNA, was forced to suggest that it came from Mars?”50
Gerald Schroeder suggests the increased supply of oxygen resulted in a tenfold improvement in the conversion of food to energy. With the new energy, organisms were able to develop more complex structures.51 These were the “abundant moving creatures in the waters” (Gen
The first fish.
Fish appeared 490 million years ago. The presence of a backbone differentiates the fish, a vertebrate, from invertebrates. But where it came from remains a mystery.
Author Arthur Strahler wrote: “Origin of the vertebrates is obscure -- there is no fossil record preceding the occurrence of fishes in the late Ordovician time.”52 Writer Francis Downes Ommanney says, “How this earliest chordate stock evolved, what stages of development it went through to eventually give rise to truly fishlike creatures we do not know. Between the Cambrian when it probably originated, and the Ordovician when the first fossils of animals with really fishlike characteristics appeared, there is a gap of perhaps 100 million years which we will probably never be able to fill.”53 The Readers Digest sums it up: “To our knowledge, no ‘link’ connected this new beast to any previous form of life. The fish just appeared.”54 But, of course. God created the fish.
Dragonflies and dragons?
God also said: “Let the waters bring forth… fowl that may fly above the earth… And… great whales” (Gen
“Fowl.” The word is translated from the Hebrew owph, meaning “to cover with wings or obscurity.” “Bird” is tsippor in Hebrew. In its commentary on Genesis 1:20, Barnes’ Notes explains: “[Bird of wing] Here the wing is made characteristic of the class, which extends beyond what we call birds.” The commentator points out that owph (“fowl”) means more than just “birds.”55
The idea is demonstrated in Leviticus 11:13-20: “And these are they which ye shall have in abomination among the fowls; they shall not be eaten, they are an abomination: the eagle, and the ossifrage, and the ospray, And the vulture, and the kite after his kind; Every raven after his kind; And the owl, and the night hawk, and the cuckow, and the hawk after his kind, And the little owl, and the cormorant, and the great owl, And the swan, and the pelican, and the gier eagle, And the stork, the heron after her kind, and the lapwing, and the bat. All fowls that creep, going upon all four, shall be an abomination unto you.”
God enumerated birds under the word “fowls,” but also included a flying mammal – the bat! Let us grant that in that pre-scientific time the Israelites did not know the difference between a true bird and a bat. Yet, in the last line we read a stranger thing: “fowls that creep, going upon all four.” Four-footed fowl? No member of the avian family creeps, much less on all fours, because birds have only two legs. The NKJV renders the verse in a more contemporary language: “All flying insects that creep on all fours…” (Lev 11:20, NKJV; also NIV and NASU).
It becomes clear that the word “fowls” lumps together true birds, a flying mammal, and flying insects -- even if they are biologically unrelated. It shows that owph refers to any creature that flies! Science asserts: “There is no fossil evidence of primitive wings prior to the appearance of fully developed winged insects...”56
Thus, the “fowl” from the waters in Genesis 1:20-22 may have actually been winged insects, prehistoric predecessors of modern dragonflies, mosquitoes, and similar insects which lay their eggs and spend the larval stages of their lives in the water!
Great whales. The “great whales” God created, rendered “great sea creatures” in NKJV and NIV, and “great sea monsters” in NASU and ASV, is hataninim hagadolim in the original Hebrew text.
In other Bible verses, the translation is “dragons”: “Praise the LORD from the earth, ye dragons (taninim)…” (Ps 148:7a); “Thou shalt tread upon the lion and adder: the young lion and the dragon (tanin)…” (Ps 91:13; Ps 74:13, Deut 32:33, Jer 9:11). Elsewhere, the translation is “serpents”: “And Moses and Aaron went in unto Pharaoh, and they did so as the LORD had commanded: and Aaron cast down his rod before Pharaoh, and before his servants, and it became a serpent (tanin)… For they cast down every man his rod, and they became serpents (taninim)…” (Ex 7:10,12a).
“Dragons” and “serpents” are both reptiles. Hence, the Hebrew taninim hagadolim (“great whales”) must have actually been huge sea reptiles -- marine dinosaurs – the sea serpents of ancient legends!
____________________
(Excerpted from Chapter 4, Primordial Planet Puzzles, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Primordial Planet Puzzles (Part 5)
Day 6: Mammals, creeping things, man
“And God said, Let the earth bring forth the living creature after his kind, cattle, and creeping thing, and beast of the earth after his kind: and it was so. And God made the beast of the earth after his kind, and cattle after their kind, and every thing that creepeth upon the earth after his kind: and God saw that it was good” (Gen 1:24-25).
Interpretations of Day 6:
- Literal 24-hour Days: the day man was created circa 6,000 years ago
- Thousand-Year Days: circa 7,000-6,000 years ago
- Diminishing Day-Ages: circa 468,750,000-13,306 years ago (Duration: approximately 468,735,694 years)
Young Earth Creationists claim land animals and man first walked on earth some 6,000 years ago, or 7,000-6,000 years ago at the earliest.
In the Diminishing Day-Ages timeline, God created land animals and hominids during Day-Age 6, 468,750,000 to 13,306 years ago (kya).
A multi-segmented Day 6?
In the Diminishing Day-Ages timeline, the sixth segment should be Day-Age 6, ending about 234,375,000 years ago after the creation of land animals (amphibians, insects, reptiles, mammals). But it cannot be the Biblical Day 6, because it ended before man could be created.
However, if we continue with the exponentially regressing pattern, we see the coming of hominids in the succeeding segments until around 28,611 years ago. For still unclear reasons, it appears that the time segments after Day-Age 5 are not individual day-ages, but parts of a multi-segmented Day-Age 6! There is no apparent basis, but the time segments match the scientific estimates accurately.
There is a clue in the Bible, though. More time and words were used to relate the events of Day 6, because more things happened and more entities were created on that last creative “day.” Moreover, there is a textual parallel in the next chapter, where one “day” is used to mean several days: “These are the generations of the heavens and of the earth when they were created, in the day that the LORD God made the earth and the heavens” (Gen 2:4). We know that the “the earth and the heavens” were not created in one single “day,’ but over several “days.”
Did God (Elohim) use more segments of time for Day-Age 6 to create animals of a higher order, as well as to perfect man -- the prime paradigm of His creative work? Let go through those time segments.
Day-Age 6-a
- Circa 468,750,000 to 234,375,000 years ago (Duration: approximately 234,375,000 years)
First of worst extinctions. Paleontologists have identified at least 17 mass extinctions since life began on earth. Eight are major, all of which took place in the last 500 million years. However, five events are the most devastating: the first took place around 438 million years ago during Day-Age 6-a. Over 85% of species became extinct.57
Amphibians created. God created land animals and “creeping things” on Day 6. Fossil remains show that amphibians, a kind of creeping creature, crawled onto dry land around 417 million years ago during Day-Age 6-a.
Second of worst extinctions. The second of the five worst mass extinction events also happened during Day-Age 6-a, approximately 367 million years ago. This time, 82% of all species were lost.58
Insects created. God created insects approximately 350 million years ago during Day-Age 6-a. Scientists are puzzled why insects, comprising 80% of all living and extinct animal species, have no known evolutionary ancestors.
A U.S. government reference (Insects, 1952) states: “There is… no fossil evidence bearing on the question of insect origin; the oldest insects known show no transition to other arthropods.”59
Reptiles created. God created more “creeping things” – reptiles. The record of the rocks reveals that cold-blooded saurians, the forerunners of modern lizards, arose on the face of the planet starting approximately 323 million years ago during Day-Age 6-a.
Mammals created. God created warm-blooded mammals -- the “beasts of the earth” (wild animals) and “cattle” (domestic animals).
The fossil record shows that the mammals first walked upon the earth 248 million years ago during Day-Age 6-a.
Third of worst extinctions. The third and most devastating of the five worst mass extinctions also occurred during Day-Age 6-a, some 245 million years ago. As much as 96% of all species were wiped out.
The destruction was so great paleontologists use this event to mark the end of the ancient or Paleozoic Era and the beginning of the middle or Mesozoic Era, when many new groups of animals arose.60
Day-Age 6-b
- Circa 234,375,000 to 117,187,500 years ago (Duration: approximately 117,187,500 years)
Fourth of worst extinctions. The fourth of the five worst mass extinctions transpired some 208 million years ago, claiming about 76% of all species at the time, including many reptiles.61
Archaeopteryx appeared. A chimeric creature appeared 150 million years ago. Scientists say it was the first true bird – with feathers and wings, and a “wishbone” (the fused collarbones underpinning wing muscles). However, it also had jaws with teeth, claws on its wings, and a long tail like dinosaurs. It was half-bird, half-reptile – the archaeopteryx!
It seems to be alluded to in Scripture. Leviticus 11:18 (NKJV) lists birds: “the white owl, the jackdaw, and the carrion vulture.” The “while owl” is tanshemeth in the Hebrew original. Several verses later, 11:30 lists reptiles: “the gecko, the monitor lizard, the sand reptile, the sand lizard, and the chameleon.” Strangely, “chameleon” is also tanshemeth in the original. The word tanshemeth, applicable to both a bird and a reptile, perfectly describes the archaeopteryx! Was tanshemeth the Scriptural term for the archaeopteryx?
Day-Age 6-c
- Circa 117,187,500 to 58,593,750 years ago (Duration: approximately 58,593,750 years)
Fifth of worst extinctions. The fifth and most recent of the five worst mass extinctions occurred more or less 65 million years ago, with the death of 76% of all species, most notably the dinosaurs.62
Primates created. Around the time that “terrible lizards” (dinosaurs) became extinct, primates – animals that resemble modern lemurs, monkeys, and apes – came onto the scene some 65,000,000 years ago during Day-Age 6-c.
Day-Age 6-d
- Circa 58,593,750 to 29,296,875 years ago (Duration: approximately 29,296,875 years)
Rise of mammals. As the level of atmospheric oxygen continued to rise from 10% to 17% about 50 million years ago, then 23% some 40 million years ago, mammals dominated the planet.
Paul Falkowski, a marine science professor, explains: "In the fossil record, we see that this rise in oxygen content corresponds exactly to a really rapid rise of large, placental mammals… The more oxygen, the bigger the mammals… the rise in oxygen content allowed mammals to become very, very large – mammals like 12-foot-tall sloths and huge saber-toothed cats.”63 Some hornless rhinoceroses measured about 30 feet long and stood 18 feet high at the shoulder.
Day-Age 6-e
- Circa 29,296,875 to 14,648,437 years ago (Duration: approximately 14,648,437 years. From here on, fractions are added to succeeding numbers to keep figures rounded.)
Day-Age 6-f
- Circa 14,648,437 to 7,324,218 years ago (Duration: approximately 7,324,218 years)
Manlike creatures.
The Jewish philosopher Maimonides said in his exegesis of Genesis that there were manlike creatures before Adam.64 Similarly, the Talmud and other ancient Jewish commentaries mention pre-Adamic animals with human forms but without the neshamah or God-given spirit.65 How did they know that before fossils were discovered?
Anthropologists call manlike creatures thought to be ancestors of man “hominids.” They call living apes “hominoids,” because they are only similar to humans, but not man’s supposed ancestors.
Ramapithecus, 14-8 mya. Found in 1932 in northern India (now part of Pakistan), parts of a fossilized jaw and some teeth, dated about 14-8 million years old, were named Ramapithecus -- “Rama's ape,” after Rama, a mythical prince of India, combined with pithekos, Greek for “ape.” In 1976, a complete jaw was discovered. With a distinctly simian V shape, it differs markedly from the parabolic shape of hominid jaws.66 More complete fossils have been found in China and Pakistan, confirming that Ramapithecus was not a hominid, but a true ape.67
Day-Age 6-g
- Circa 7,324,218 to 3,662,109 years ago (Duration: approximately 3,662,109 years)
Sahelanthropus tchadensis, 7-6 mya. In 2001 the fossils of the supposedly oldest hominid species, estimated at 7-6 million years old, were found in the north central African nation of Chad.68 Dubbed Sahelanthropus (“Sahel man,” after the semi-arid region and the Greek word anthropos, meaning “human”), it has an apelike skull. The fossil pieces are so few, it is uncertain if Sahelanthropus walked bipedally.69
Orrorin tugenensis, 6 mya. Found in the Tugen Hills of central Kenya in 2000, the fossils received the name Orrorin tugenensis, which means “original man in the Tugen region.” Thought to be 6 million years old,70 the fossilized skeleton has simian features, including long, curved finger bones for grasping and movement in trees, and apelike canine and premolar teeth.71
Ardipithecus, 4.4 mya. Unearthed in Ethiopia in 1994, this fossil find dated to be 4.4-million years old has been named Ardipithecus, from words in the Afar and Greek languages meaning “ground ape.”72 “Ardi,” however, has apelike teeth and skeleton, suggesting its ability to walk upright might not have been well developed.73
Australopithecus, 4-1 mya. In 1924, a fossilized skull was dug up in Taung, South Africa. It was named Australopithecus, which means “southern ape.” Thought to be man’s ancestor, six species have since been identified. An almost complete 3,200,000-year-old skeleton of a female unearthed in 1974 by Donald Johanson at Hadar, Ethiopia, was nicknamed “Lucy,” after the Beatles song “Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds,” which played on the night of the find.74
Australopithecines, some 3½ to 5 feet tall, had a brain (390-550 cu cm) about one-third of that of a modern human; a low cranium behind a projecting face; small canine teeth like those of humans, but large cheek teeth (molars) like apes. Although Lucy had arms proportionally longer than those of modern people, she is said to have walked upright,75 based on a knee joint. (Johanson later said the knee fragment was discovered a mile and a half away in a rock layer 200 feet deeper, but was included due to “anatomical similarity.”)76
Bruce Bower, in the Science News of 2 June 2001, reported that, in one study, Australopithecine inner ear bones used to maintain balance were found to be greatly similar to those of chimpanzees and gorillas, but markedly different from those of humans.77 Mark Cartmill et al. wrote in the July-August 1986 issue of American Scientist: “At present we have no grounds for thinking that there was anything distinctively human about australopithecine ecology and behavior... they were surprisingly apelike in skull form, premolar dentition, limb proportions, and morphology of some joint surfaces, and they may still have been spending a significant amount of time in the trees.”78
Anatomist Sir Solly Zuckerman and Dr. Charles Oxnard, in contrast to anthropologists using subjective and less analytical visual techniques, developed a multivariate analysis technique with computers performing millions of analyses on homologous Australopithecine, simian, and human bones. Their finding: Australopithecus is not a missing link between ape and man.79 Sir Solly observed: “When compared with human and simian skulls, the Australopithecine skull is in appearance overwhelmingly simian – not human… Our findings leave little doubt that… Australopithecus resembles not Homo sapiens but the living monkeys and apes.”80
Paleontologist Richard Leakey said in his book Origins (1977) that it is “unlikely that our direct ancestors are evolutionary descendants of the australopithecines.”81 James Shreeve remarked in the Science magazine issue of May 3, 1996: “The proportions calculated for (Australopithecus) africanus turned out to be amazingly close to those of a chimpanzee, with big arms and small legs... One might say we are kicking Lucy out of the family tree…”82 As their family name pithecus (“ape”) denotes, these prehistoric pithecoid creatures were just apes.
Day-Age 6-h
- Circa 3,662,109 to 1,831,054 years ago (Duration: approximately 1,831,054 years.)
Kenyanthropus platyops, 3.5 mya. A fossilized cranium and other bones, estimated to be 3.5 million years old, were found in 1999 in northern Kenya. The creature had a mixture of features not seen in earlier hominid fossils: a much flatter face and smaller molars; the cheekbone joined the rest of the face in a forward position; and the region beneath the nose opening was flat. Researchers placed it under a new genus and species: Kenyanthropus platyops. In Greek anthropos means “humen being,” while platyops means “flat” – combined to mean “flat-faced human from Kenya.”83
Homo habilis, 2.8-1.5 mya. So named for the primitive stone tools found with its fossilized skull in 1960, Homo habilis means “handy man” -- from Latin words meaning “human” (homo) and “able or skillful” (habilis). The first to be classified under the genus Homo, the species had a bigger braincase of about 600 cu cm.84 It was also taller.
The fossil had been found beneath volcanic ash dated at about 2.6 million years, pushing back the presumed origin of man by millions of years. Its discoverer, Richard Leakey, says: “Either we toss out this skull or we toss out our theories of early man.” He adds that “it leaves in ruins the modern notion that all early fossils can be arranged in an orderly sequence of evolutionary change.”85
The first confirmed limb bones of Homo habilis were discovered in 1986. They showed the creature clearly had apelike proportions and should never have been classified as human. Hugh Ross comments on the web: “Starting about 2-4 million years ago, God began creating man-like mammals or ‘hominids.’ These creatures stood on two feet, had large brains, and used tools. Some even buried their dead and painted on cave walls… God replaced them with Adam and Eve.”86
Homo rudolfensis, 1.9 mya. In 1972, more than 150 fragments of bone fossils were discovered in eastern Kenya. As the size of the skull and several anatomical features differed from those of earlier finds, scientists classified it under a new species named Homo rudolfensis, after Lake Rudolf (now Lake Turkana). Its best-known fossils from the lake area date from about 1.9 million years ago.87
Richard Leakey notes: “This Australopithecine material suggests a form of locomotion that was not entirely upright nor bipedal. The Rudolf Australopithecines, in fact, may have been close to the ‘knuckle-walker’ condition, not unlike the extant African apes.”88
Day-Age 6-i
- Circa 1,831,054 to 915,527 years ago (Duration: approximately 915,527 years)
Homo erectus, 1.5 mya. A skullcap and tooth found in 1891 by Eugene Dubois in the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) was first named Pithecanthropus erectus (“erect ape-man”). Popularly known as “Java man,” it is dated about 1,500,000 years old. It had a larger brain (about 850 cc) and a rounder cranium than earlier species.89
In China, at a site known as Chou K’ou Tien (Dragon-Bone Hill), 25 miles from Peking, from 1921 to 1934 a total of 14 skull fragments, 11 jawbones, 7 thigh pieces, 2 arm bones, a wrist bone, and 147 teeth similar to Java Man were found. Called Sinanthropus pekinensis – “Peking Man” – its composite skull was named “Nellie.”90
Forty years after finding “Java man,” Dubois conceded it was a big ape. “Pithecanthropus was not a man, but a gigantic genus allied to the Gibbons, superior to its near relatives on account of its exceedingly large brain volume, and distinguished at the same time by its erect attitude.”91 He admitted withholding parts of four simian thigh bones found in the same area.
The World Book states: “Modern humans could not have evolved from these late populations of H. erectus, a much more primitive type of human.”92
Day-Age 6-j:
- Circa 915,527 to 457,763 years ago (Duration: approximately 457,763 years)
Homo heidelbergensis, 600-300 kya. In 1907 a fossilized manlike jaw was discovered 16 kilometers southeast of Heidelberg, Germany. It had no chin, but was unusually thick and broad, as well as long, suggesting the individual had a projecting lower face. The teeth also were too small for the massive mandible.
Other specimens from Africa (Ethiopia, Zambia, Tanzania), Europe (Greece, France), and possibly Asia (China) have been dated at from approximately 600 to 300 thousand years ago (kya).93 Their craniums have heavy brow ridges, long and low braincases, and thick vault bones like H. erectus, but larger.
____________________
57Mass Extinctions, Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
(Excerpted from Chapter 4, Primordial Planet Puzzles, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Primordial Planet Puzzles (Part 6)
The image of God
“And God said, Let us make man in
our image, after our likeness: and let them have dominion over the fish of the
sea, and over the fowl of the air, and over the cattle, and over all the earth,
and over every creeping thing that creepeth upon the earth” (Gen 1:26).
Science
and Scripture are again in complete agreement: human beings were the last form
of living creatures to appear on earth.
A
“plural” God?
Oddly,
God spoke in the first person plural: “let
us… in our image… after our likeness…” Apart from the verse above, God’s
reference to Himself in the plural is seen in a few other Biblical verses: Genesis
3:22 (“And the LORD God said, Behold, the
man is become as one of us…”); Genesis
11:7 (“Come, let us go down and confuse
their language…”); Isaiah 6:8 (“Also
I heard the voice of the Lord, saying, Whom shall I send, and who will go for
us?”).
Some
scholars say God referred to Himself in the plural, because the Godhead is said
to have three Persons – the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit. Others
suggest the way He spoke was “communicative
(including the attendant angels),”94 that is, God was speaking for
both Himself and the angels in His presence. In Genesis 3:22, the phrase “one of us” in both Hebrew and the
literal English translation clearly means one among many. We can only conclude
that by “us” God means Himself plus others who were with Him.
God and “gods.” In the Scriptures, the word “God”
is usually translated from the Hebrew elohim
(“gods”), the plural form of El and
its variants Elah, Eloah, Eloha. Scholars
“interpret the –im ending as an
expression of majesty (pluralis
majestatis) or excellence (pluralis
excellentiae), expressing high dignity or greatness…”95 Others
disagree. “Theologians who dispute this cite the hypothesis that plurals of
majesty came about in more modern times. Richard Toporoski, a classical
scholar, asserts that plurals of majesty first appeared in the reign of
Diocletian (284-305 CE)… The use of the plural as a form of respectful address
is quite foreign to Hebrew.”96
In Psalm
82, the angels are called “gods” (elohim):
“God (Elohim) standeth in the
congregation of the mighty (el); he judgeth among the gods (elohim)… I have
said, Ye are gods (elohim); and all of you are children of the most High” (Ps
82:1,6).
In
Psalm 149:2, the English word “Maker” was actually “Makers” in the Hebrew
original, as indicated by the plural verb. It thus should read: “Let
God
showed Himself to Abraham as three angels. “And
the LORD appeared unto him in the plains of Mamre: and he sat in the tent door
in the heat of the day; And he lift up his eyes and looked, and, lo, three men
stood by him: and when he saw them, he ran to meet them from the tent door, and
bowed himself toward the ground” (Gen 18:1-2).
In view
of the above, did God have angels acting for Him during the Creation? The Angel
of the LORD? Moreover, do the terms “image”
and “likeness” imply that the Angel
of the LORD and the angels have a physical form after which they fashioned man?
Physical
resemblance?
The
terms “image” and “likeness” may have two implications:
First, they could signify that man, or at least a part of him, has been made a
spirit like God and the angels. Second, they could mean that man has been
patterned after the physical configurations of the Creator (the Angel of the
LORD) and the angels, literally.
The terms
are used at least once in the Bible in the physical sense: “And Adam lived an hundred and thirty years,
and begat a son in his own likeness, after his image; and called his name Seth”
(Gen 5:3). The Interpreter’s
Dictionary of the Bible explains: “Man’s resemblance to God is analogous to
Seth’s resemblance to his father Adam. This makes it certain that physical
resemblance must not be excluded.”97
The form of angels. If God and the angels were
spirits, why did God create the physical universe? Of what use would it be to
them? God also planted a garden in
The
Scriptures hint angels can change their physical forms. In Psalm 68:17 (“The chariots of God are twenty thousand,
even thousands of angels [shin’an]…”),
the Hebrew word used for angels is shin’an,
the root meaning of which is “to
change or alter.” This strongly
suggests angels can change or alter their forms at will.
As
we know, God and the angels descended to earth from time to time in physical
form. Of all organic structures, the human figure appears to be the most
suitable and most efficient design for the terrestrial setting. James, Christ’s
own brother, reiterates that the human form has been patterned after that of
God: “Therewith bless we God, even the
Father; and therewith curse we men, which are made after the similitude of God”
(James 3:9).
One kind, several forms. If man was created in the “image” and “likeness” of God, how can the appearance of various manlike creatures
before Adam be explained?
The
Torah account tends to skip over some details to simplify the narrative, as we
have seen earlier. On Day 6 amphibians, reptiles and insects are lumped together
under just one term: “creeping things”
(Gen
Similarly,
it looks like Genesis 1:26 has grouped together in one word – “man” – all the different species of
subhumans and hominids, different versions and “likenesses” of the same type which
eventually culminated in Adam, the crowning glory of God’s creation.
Day-Age 6-k:
- Circa 457,763 to 228,882
years ago (Duration: approximately 228,882 years)
Homo
Neanderthalensis, 300 kya. In 1856 workmen found
fossil bones in a limestone cave in the Neander valley (thal), near
Over 60
more similar fragments have since been unearthed in other parts of
At first
scientists thought Neanderthals had a crouching and apelike posture. They later
realized some of the bones bore signs of arthritis and rickets.
They concluded that Neanderthals actually walked upright, not stooped on bent
knees. Recent dental and x-ray studies suggest they matured at a slower rate,
but lived longer than people today.
Neanderthals
used fire, made stone tools and leather, played music (indicated by a wooden
flute), cared for the injured and elderly (bones show survival to old age after
suffering wounds, fractures, diseases, even blindness).101 They
seemed to have worshipped bears and buried their dead, covering them with
flowers.
In
1997, researchers announced they had extracted a small amount of DNA from a
Neanderthal fossil. They “compared the Neandertal DNA sequence to sequences in
the same region of DNA for 994 modern human lineages, which included
Australians, Pacific Islanders, Africans, Asians, Native Americans, and
Europeans. The Neandertal DNA sequence differed from all the modern human DNA
by either 27 or 28 base pairs. In comparison, modern human sequences in this
region of DNA differ from each other on average by 8 base pairs.”102
The DNA evidence, the World Book
says, supports the belief that the Neanderthals were a separate species and not
ancestors of modern humans.103
Day-Age 6-l:
- Circa 228,882 to 114,441
years ago (Duration: approximately 114,441 years)
Day-Age 6-m:
- Circa 114,441 to 57,221 years
ago (Duration: approximately 57,221 years.)
Homo
sapiens, 200-100 kya. In 1868, fossilized
human bones were discovered in the Cro-Magnon cave in southwestern
Also
called “Cro-Magnon man,” more than
100 specimens have since been found. A population appears to have lived in
Finely
shaped artifacts reveal the Cro-Magnons had mastered the techniques of making useful
objects from stone, bone, shell, and clay, such as tools, trinkets, lamps,
needles. They wore fitted clothes, jewelry, and other ornaments.106 Most
notably, they produced beautiful paintings of animals in the caves of southwestern
Like
Neanderthals, Cro-Magnons buried their dead. This suggests they believed in an
other world of spirits. After all, the Creator had spoken to them: “And God blessed them, and God said unto
them, Be fruitful, and multiply, and replenish the earth, and subdue it: and
have dominion over the fish of the sea, and over the fowl of the air, and over
every living thing that moveth upon the earth” (Gen
No relation. Remains of Cro-Magnons and the
older Neanderthals overlap in the fossil record, showing the two species lived
alongside each other for a long period of time – no less than 70,000 years.
This precludes any notion that Cro-Magnons evolved from Neanderthals.
Neither
did modern man. Neanderthals had an ear canal (labyrinth, three hollow rings
involved in balance) that was distinctly different in size and location from that
of people today. The Word Book notes:
“Because the features of the Neandertal's labyrinth do not exist in modern
humans, the scientists believe that the muscular hominid belongs to a separate
species, or at least is not an ancestor of modern humans.”107
Researchers
have extracted DNA samples from a 40,000-year-old human skeleton (from the Cro-Magnon
era) found at
____________________
94Names of God,
Kabbalah, Wikipedia, Internet
95Ibid.
96Ibid.
97The Interpreter’s Dictionary of the Bible, p. 683
98David Menton, “Did
Humans Really Evolve from Apelike Creatures?”, The New Answers Book 2, 2008, p. 91
99Mitochondria,
“Neandertals Were Not Close Relations, Say DNA Test,” Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
100Human Evolution, Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
101David Menton, “Did
Humans Really Evolve from Apelike Creatures?”, The New Answers Book 2, 2008, p. 92
102Homo
Neanderthalensis, “Neandertals Were Not Close Relations, DNA Testing Finds,” Encyclopaedia Britannica 2009 Student and
Home Edition
103Prehistoric people, World Book 2005 (Deluxe)
104Human being, World Book 2005 (Deluxe)
105Cro-Magnon, Encyclopaedia Britannica 2009 Student and
Home Edition
106Cro-Magnon, Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
107Neanderthals, World Book 2005 (Deluxe)
108Prehistoric People, loc. cit.
(Excerpted from Chapter 4, Primordial Planet Puzzles, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Primordial Planet
Puzzles (Part 7)
A vegetarian world
“And God said, Behold, I have given you every herb bearing seed, which is upon the face of all the earth, and every tree, in the which is the fruit of a tree yielding seed; to you it shall be for meat. And to every beast of the earth, and to every fowl of the air, and to every thing that creepeth upon the earth, wherein there is life, I have given every green herb for meat: and it was so” (Gen
Were plants and fruits alone sufficient to have kept the first men in the excellent health necessary for long and active lives?
A well-rounded diet? Nutritionists name six kinds of nutrients: water, carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. The first four are “macronutrients” we must have in large amounts. Much water is needed, since the body is 50-75% water. A lot of carbohydrates and fats are a must for energy; proteins for body tissues. Vitamins and minerals, the “micronutrients,” are taken in minute quantities, but are vital for growth and organ functions.
Plants and fruits have high water contents. Grains, legumes, and rootcrops are mostly carbohydrates. Oil sources, like coconut, olive, corn, soybean, sunflower, supply fats. Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals. But proteins are best obtained from animals as milk, eggs, meat, fish. These are complete proteins containing all the essential amino acids. Cereals, nuts, and vegetables, lacking one or more essential amino acids, are incomplete proteins. A primeval vegetarian diet would not have been well-rounded. Or was it?
Were all the nutrients that the first men and animals needed in the right amounts in the plants and fruits that have since become extinct? The herbivorous dinosaurs were the biggest creatures on earth and lasted for millions of years. The biggest and strongest land animals today are the plant-eating elephants, giraffes, rhinoceroses, buffaloes. Part of the dinosaurs’ diet 248-65 million years ago were leaves of the ginkgo tree, today a “living fossil” in
Flesh-eating creatures
In many paleontological digs around the globe, animal bones have been found with manlike fossils. Java and Peking man sites yielded remains of bats, monkeys, rhinoceroses, elephants, wild cats. Hominids ate many herbivores like deer, goats, and oxen, but their diet included carnivorous predators and scavengers such as lions, wolves, bears.
Traders or raiders? Archeologists believe, based on mixed artifacts found, that primitive Neanderthals may have traded with the more modern Cro-Magnons. The
Did they trade with each other or raid one another? Skeletal remains show that Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons lived in a brutal period. There were signs of violence in the form of broken bones, scars, and healed-over bone growths. In particular, there was a high incidence of neck and head injuries. The artifacts could have been spoils of war.
Man-eating men. A French-American team has unearthed evidence of cannibalism at a Neanderthal site in
Other Homo erectus, Neanderthal, and early Homo sapiens (Cro-Magnon) sites piece together the same grisly picture: With sharp stone tools, hominids dismembered and defleshed their kills. They used stone hammers and anvils to break open the big bones for the marrow. Many skulls had been bashed open to extract the brains. Evidence indicates some Neanderthals may have done the same to their relatives.
Signs of cannibalism are present in only a few sites, but because the total number of sites is small, it was statistically a widespread practice.
Day-Age 6-n:
- Circa 57,221 to 28,611 years ago (Duration: approximately 28,611 years)
Day-Age 6-o:
- Circa 28,611 to 13,306 years ago (Duration: approximately 14,306 years)
End of Day 6
“And God saw every thing that he had made, and, behold, it was very good. And the evening and the morning were the sixth day” (Gen
Day-Age 6 Summary:
- Total duration (Day-Age 6-a to 6-o): circa 468,735,694 years. (To round figures, 0.8858 remainder from the exponential regression has been added to the remaining 14,305.1142 years, for a full 14,306 years. See table at the end of this chapter.)
Day 7: Day of rest
“Thus the heavens and the earth were finished, and all the host of them. And on the seventh day God ended his work which he had made; and he rested on the seventh day from all his work which he had made. And God blessed the seventh day, and sanctified it: because that in it he had rested from all his work which God created and made” (Gen 2:1-3).
Interpretations of Day 7:
- Literal 24-Hour Days: 1 day after man was created circa 6,000 years ago
- Thousand-Year Days: circa 6,000-5,000 years ago
- Diminishing Day-Ages: circa 13,306 to 6,153 years ago (Duration: approximately 7,153 years)
Shift to 1,000-year “days”?
After the seven-“day” Creation “week,” the flow of time appears to have shifted inexplicably to a dual mode for all, as laid down in 2 Peter 3:8 (“one day is with the Lord as a thousand years, and a thousand years as one day”; cf. Ps 90:4): literal 24-hour days from man’s standpoint, and prophetic 1,000-year “days” from God’s viewpoint.
Thus, both Young and Old Earth Creationists now reckon days as 24-hour periods, but at the same time are subject to God’s 1,000-year “days” in the prophetic countdown.
Countdown to completion.
In the Diminishing Day-Ages timeline, some 7,153 years were still remaining in 4004 B.C. at the creation of modern man’s ancestor, Adam, before the full 15 billion years could be completed.
Homo sapiens sapiens. The subspecies Homo sapiens sapiens, whose first specimen was Adam, includes all people living today. The braincase of modern man ranges from about 1,000 to 2,000 cu cm (60 to 120 cu in), averaging around 1,350 cu cm (80 cu in),111 slightly smaller than those of Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons, but proportional to a less massive muscular build.
The World Book reports that, after scientifically comparing DNA samples of modern men with those of Neanderthals and other extinct hominids, many scientists conclude that the results indicate all people today form a separate species distinct from prehistoric humans.112 (The scientists, however, fell short of saying how the first man came about.)
Homo sapiens sapiens timeline.
· Circa 6,000-5,000 years ago. God created Adam some 6,000 years ago (4004 B.C.) The wheel was invented around 5,500 years ago (3500 B.C.) in Sumer, Mesopotamia,113 where an early writing system in the form of pictographs also appeared at about the same time; followed 5,300 years ago by Egyptian hieroglyphics (3300-3200 B.C.).114
· Circa 5,000-4,000 years ago. The Bronze Age began some 5,000 years ago (3000 B.C.) in
· Circa 4,000-3,000 years ago. Abraham was born about 4,000 years ago (1996 B.C.) The Iron Age began sometime around 1500-1000 B.C., with the use of iron for tools and weapons.116
· Circa 3,000-2,000 years ago. David lived and died about 3,000 years ago (1015 B.C.), followed by his son Solomon (975 B.C.).
· Circa 2,000-1,000 years ago. Christ was born about 2,000 years ago (5 B.C.). The eastern
· Circa 1,000 years ago-present. Christians launched Crusades from 1096 to 1396 to regain the
· Next 1,000 years. The Millennium, the prophesied 1,000-year era of peace (mankind’s great Sabbath of rest), during which Christ will reign on earth as King of Kings (Rev 20:1-7).
Diminishing Day-Ages Chronology
(7-“Day” Creation “Week” until 3000 A.D. = 15 Billion Years)
Day-Ages | Scriptures | Beginning, circa years ago | Science/History | Occurrence, circa years ago |
Day 1 | Light | 15,000,000,000 | Big Bang | 13,700,000,000 |
|
|
| Milky Way | 8,000,000,000 |
Day 2 | Firmament | 7,500,000,000 | Sun, Earth, Moon | 4,600,000,000 |
Day 3 | Seas, dry land, vegetation | 3,750,000,000 | Oceans; bacteria/ cells w/out nuclei | 3,500,000,000 |
Day 4 | Heavenly lights | 1,875,000,000 | Atmosphere thinned |
|
|
|
| Cells with nuclei | 1,800,000,000 |
Day 5 | Sea creatures, | 937,500,000 | Animal life forms | 700,000,000 |
| flying creatures |
| Cambrian Explosion | 544,000,000 |
|
|
| Chordates, fish | 490,000,000 |
Day 6-a |
| 468,750,000 | 85% extinction | 438,000,000 |
| Land animals |
| Amphibians | 417,000,000 |
|
|
| 82% extinction | 367,000,000 |
| Creeping |
| Insects | 350,000,000 |
| things |
| Reptiles | 323,000,000 |
| Beasts, cattle |
| Mammals | 248,000,000 |
|
|
| 96% extinction | 245,000,000 |
6-b |
| 234,375,000 | 76% extinction | 208,000,000 |
|
|
| Archaeopteryx | 150,000,000 |
6-c |
| 117,187,500 | 76% extinction | 65,000,000 |
|
|
| Primates (lemurs, | “ |
6-d |
| 58,593,750 | monkeys, |
|
6-e |
| 29,296,875 | apes) |
|
6-f |
| 14,648,437 | Ramapithecus | 14,000,000 |
6-g |
| 7,324,218 | Sahelanthropus | 7,000,000 |
|
|
| Orrorin tugenensis | 6,000,000 |
|
|
| Ardipithecus | 4,400,000 |
|
|
| Australopithecus | 4,000,000 |
6-h |
| 3,662,109 | Kenyanthropus | 3,500,000 |
|
|
| Homo habilis | 2,800,000 |
|
|
| Homo rudolfensis | 1,900,000 |
6-i |
| 1,831,054 | Homo erectus | 1,500,000 |
6-j |
| 915,527 | H. heidelbergensis | 600,000 |
6-k | Man | 457,763 | H. Neanderthalensis | 300,000 |
6-l |
| 228,882 | Homo sapiens | 200,000 |
6-m | “ | 114,441 |
|
|
6-n |
| 57,221 |
|
|
6-o |
| 28,611 |
|
|
Day 7 | Day of rest | 14,306 |
|
|
Day 8 | Adam | 6,000 | Wheel, writing | 5,500 |
Day 9 | Noah, Flood | 5,000 | Bronze Age | 5,000 |
Day 10 | Abraham | 4,000 | Iron Age | 3,500 |
Day 11 | David, Solomon | 3,000 | 2,750 | |
Day 12 | Christ | 2,000 | Dark/Middle Ages | 1,600 |
Day 13 | (Crusades) | 1,000 | Modern Age | 250 |
Day 14 | Millennium/rest | (near future) |
|
|
__________________
109.Nature, May 16, 1996
(Excerpted from Chapter 4, Primordial Planet Puzzles, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Early Earth Enigmas (Part 1)
The universe appears to have been mathematically designed. Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who taught that the universe was built upon numbers, is known to have said: “Nature geometrizes.”1
Sir Jonathan Sacks, Chief Rabbi, United Hebrew Congregations of the Commonwealth, is awed: “The believer might wonder, as does Lord Rees, president of the Royal Society, in his Just Six Numbers, at the extraordinary precision of the six mathematical constants that determine the shape of the Universe, such that if even one were fractionally different neither we nor the Universe would exist.”2
Nobel laureate for physics Steven Weinberg concurs: “Life as we know it would be impossible if any one of several physical quantities had slightly different values… One constant does seem to require incredible fine tuning.” He quantifies the tuning as one part in 10120!3
Sir James Jeans, knighted British physicist, once remarked: “From the intrinsic evidence of His creation, the Great Architect of the Universe now begins to appear as a pure mathematician.”4
Isaiah expresses the same thought in enigmatic terms: “Who has measured the waters in the hollow of His hand, Measured heaven with a span And calculated the dust of the earth in a measure? Weighed the mountains in scales And the hills in a balance? (Isa 40:12, NKJV).
“Anthropic” planet
Earth, a tiny planet, is just one of the countless objects in the vastness of space, yet it is the only one known to support life. Scientists are puzzled by the numerous “accidents” that favor life on earth. Many conclude that Earth is “anthropic” -- that is, “specially made for man.”
Size of the Earth.
The scientific data suggest that the Earth did not randomly come into existence. It has precise measurements that look like the product of careful planning and design. So said God to Job: "Where were you when I laid the foundations of the earth? Tell Me, if you have understanding. Who determined its measurements? Surely you know! Or who stretched the line upon it?” (Job 38:4-5, NKJV).
If the Earth were larger, gravity would be stronger. Hydrogen would be unable to escape from the surface and collect in the atmosphere, rendering the planet inhospitable to life. If the Earth were smaller, gravity would be weaker. Oxygen would escape into space, and animals could have never emerged on the planet.
Location and motion.
Astrophysicist Paul Davies, in his book The Goldilocks Enigma (2007), nicknamed the Earth “the Goldilocks Planet.” It has just the right temperature, neither too hot nor too cold.5
Distance from the sun. The Earth lies at an ideal distance from the Sun: 93,000,000 miles (150,000,000 km) away. If the distance changed by as little as 2%, all life on Earth would perish. If the Earth were a bit farther from the sun, water would freeze; a little closer, water would evaporate. Consider our neighbors: Venus, closer to the Sun, is too hot; while Mars, farther away, is too cold.
Earth’s orbit. The Earth’s orbit around the Sun is just about 3% off a perfect circle – just right to keep water liquid. If its orbit were as elliptical as that of Mars, water would alternately boil when we are nearest to the Sun and freeze when we are farthest.
The Earth orbits the sun at a speed of about 66,600 miles per hour. That velocity is perfect to offset the gravitational pull of the sun, as well as keep the earth at an ideal distance. If the speed were slower, the Earth would be gradually pulled toward the sun, eventually having all life scorched to extinction. If faster, the Earth would move farther and farther away from the sun, and eventually become a frozen wasteland.
Rotation and axis. The Earth’s rotation period cannot be changed by even just a few percent. Too slow, the temperature differences between night and day would be too great. Too fast, wind velocities would become disastrous.
The tilt of the Earth’s axis is at a 23.5o angle relative to the sun. Greater, summers would be much hotter and winters much colder, wreaking havoc on plant cycles and agriculture.
Neighboring objects. For a satellite, the moon is too big for the Earth. And, yet, it is just the right size. Its gravitational pull produces the tides that prevent the oceans from either boiling or freezing. Coastal waters are cleansed, oxygen and nutrients which sustain marine life are replenished, and the tilt of the Earth is stabilized.
The gargantuan planet Jupiter, with its massive gravitational force, occupies a nearby location that is favorable to our planet. Otherwise, Earth would be struck about a thousand times more frequently by asteroids, comets, and space debris.
Atmosphere and magnetosphere.
Oxygen. This life-sustaining gas comprises 21% of the Earth’s atmosphere. Much more than that would be harmful – oxygen could be toxic if breathed too long, as well as make the environment fire-prone.
Ozone, an unstable oxygen molecule, forms a layer in the top level of the atmosphere. The ozone layer blocks most of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation that can burn sensitive skin, damage eyes, and cause cancer.
Nitrogen. This constitutes 78% of the gases surrounding the planet. It dilutes the oxygen, serving as a fertilizer for plant life. Lightning bolts around the world mix nitrogen with oxygen each day, producing compounds that come down to earth with rain and enrich the soil.
Carbon dioxide. The amount of this gas in the atmosphere (3/100 of 1%) is just right – less would not be enough to keep vegetation thriving; more, say 10%, would be fatal to both animals and humans.
All the other necessary elements are present – carbon, hydrogen, phosphorous, sulfur, as well as liquid water -- in the right proportions, as though deliberately combined. Science writer Stuart Clark wonders: “Chemically speaking, Earth is simply better set up for life than its neighbors. So how come we got all the good stuff?”6
Magnetosphere. The Earth has just enough internal radioactivity to maintain its iron core in a molten state,7 thus creating a protective force field surrounding the planet as far as 40,000 miles out. The magnetosphere protects the Earth against cosmic radiation.
Isaiah tells us why God did all these: “For this is what the LORD says -- he who created the heavens, he is God; he who fashioned and made the earth, he founded it; he did not create it to be empty, but formed it to be inhabited…” (Isa 45:18a, NIV).
The air we breathe
When the Earth became a solid body, about 4.6 billion years ago, the atmosphere is believed to have consisted solely of volcanic emissions -- a mixture of water vapor (85%), carbon dioxide (10%), sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen, with almost no oxygen.8
Rise of oxygen.
Around 2.4 billion years ago, new marine microorganisms capable of photosynthesis (primitive plants) began splitting water molecules to produce oxygen using the sun's energy.9
Subsequently, oxygen escaped from the oceans to the atmosphere, starting the formation of the ozone layer, which acted as a sunscreen that reduced harmful ultraviolet rays striking the oceans. This allowed photosynthetic bacteria that previously lived in the depths to move up to the surface and increase the output of oxygen.10
About 100 million years later, organisms with 2-3 different cell types and deriving energy from oxygen appeared. Then followed more complex cells equipped with mitochondria (sausage-shaped structures that produce energy in cells).11 Further increases of oxygen in the air led to the emergence of new air-breathing marine animals approximately 570 million years ago.12
Bigger creatures.
The availability of more oxygen greatly enhanced the metabolic efficiency of organisms in extracting nutrients from food and converting them to energy. Many marine creatures grew to enormous sizes. Chambered nautiluses that are eight inches wide today measured nine feet across.13 On land, cockroaches were about a foot long. Dragonflies had wings almost three feet in span.14
Air bubbles in amber (fossil resin from trees) strongly suggest that oxygen in the atmosphere might have been as high as 25%.15 Then, in the last 10 million years, atmospheric oxygen went down to its present level of 21%. Why?
Some scientists speculate that great fires burned over the earth about 10 million years ago, reducing the number of trees and, consequently, the amount of photosynthesis and oxygen.16
The wonders of water
Earth is the only planet positively known to have liquid water. The most abundant substance on earth, water covers approximately 71% of the planet’s surface.
Water is essential to life. Combined with carbon and certain other key elements, water is the basis of almost all the molecules of living organisms. Fluids primarily made up of water, like sap and blood, carry the vital materials that plants, animals, and humans need to live. Water is an ideal solvent for metabolism as it dissolves the food that sustains living organisms.
Where all the water came from remains an enigma. If the solar system and the Earth had formed from clouds of gases and dust, hardly any water would be found on Earth. Any water this close to the Sun would have been vaporized and blown away by the solar wind, like water vapor in the tails of comets.
Law of nature altered?
Most liquids contract as their temperature goes down. So, too, water. As it gets colder, water in rivers, lakes, and seas becomes denser and heavier, sinking and forcing the lighter, warmer water beneath to rise to the top. Yet, on reaching precisely 7oF (4oC) above zero, the process is inexplicably reversed! Water begins to expand until frozen into ice, its volume increasing by 10%. Being lighter, ice floats above liquid water.
The ice on the surface serves as an insulator that keeps the water below from freezing, protecting organisms beneath. If water did not stop contracting just before freezing point, ice would be heavier and sink to the bottom, where the sun's heat could not melt it. Eventually, layers upon layers of ice would pile up, turning the Earth into an ice planet.
Did God recalibrate a law of nature to make Earth hospitable to life? This reminds us of what He said through Jeremiah: “For I know the plans I have for you," declares the LORD, "plans to prosper you and not to harm you, plans to give you hope and a future” (Jer 29:11, NIV).
____________________
1Quoted by Migene Gonzalez-Wippler, A Kabbalah for the Modern World, 1974, p. 16
2Jonathan Sacks, “Genesis and the origin of the Origin of the species,” The Times (London), August 29, 2008
3Steven Weinberg, “Life in the Universe,” Scientific American, October 1994
4Sir James Jeans, The Mysterious Universe, 1930
5Paul Davies, The Goldilocks Enigma, 2007
6Stuart Clark, “Unknown Earth: Our Planet’s Seven Biggest Mysteries,” New Scientist, Sept. 7, 2008
7Gerald Schroeder, The Science of God, 1997, p. 191
8Atmosphere, Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
9ScienceDaily, Mar. 22, 2006, Internet
1“Rise Of Oxygen Caused Earth's Earliest Ice Age,” ScienceDaily, May 7, 2009, Internet
11“Oxygen Triggered The Evolution Of Complex Life Forms,” Exo Life, Jan 29, 2004, Internet
12Atmosphere, loc. cit.
13National Geographic, January 1976; quoted by Dennis Petersen, Unlocking the Mysteries of Creation, p. 100
14Dennis Petersen, Unlocking the Mysteries of Creation, 2002, pp. 32-33
15Petersen, op. cit., p. 35
16“Oxygen Increase Caused Mammals To Triumph, Researchers Say,” ScienceDaily, Oct. 3, 2005, Internet
(Excerpted from Chapter 5, Early Earth Enigmas, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Early Earth Enigmas (Part 2)
First life forms
Scientists
believe life on earth began in the water. Charles Darwin, who advanced the
theory of evolution in his 1859 book On
the Origin of Species, once wrote to a friend that life might have begun in
“some warm little pond.” His evolutionary theory assumes that, billions of
years ago, microscopic life spontaneously appeared.
Spontaneous generation?
Richard Dawkins, an atheist, summarizes the idea in his
book, The Selfish Gene (1976): “The
newly formed Earth had an atmosphere made up of carbon dioxide, methane,
ammonia, and water. These simple compounds were broken up by energy from
sunlight, lightning, and exploding volcanoes, then reformed into amino acids.
These accumulated in the sea and combined into protein-like compounds, producing
a potentially ‘organic soup.’ Then, ‘a particularly remarkable molecule was
formed by accident’ – a molecule that had the ability to reproduce itself.”
(The accident, the author admitted, was exceedingly improbable.) Similar
molecules clustered together, and then, by an exceedingly improbable accident
again, wrapped a protective barrier of other protein molecules around
themselves as a membrane. Thus, it is thought, the first “living” cell
generated itself. (In the preface to his book, Dawkins says: “This book should
be read almost as though it were science fiction.”)17
The
first organic molecules are said to have been simple sugars and amino acids,
the building blocks of proteins. Proteins, in turn, are the building blocks of
living cells. The first living cell is presumed to have been anaerobic
(surviving without oxygen), using methane for energy.18
The
sudden appearance of life all by itself from non-living matter is called
“spontaneous generation” or abiogenesis,
which comes from the Greek words a (“without”),
bio (“life”) and genesis (“birth”). However, this theory violates the law of
biogenesis, which states that all life must come from preceding life of its
kind.
Spontaneous dissolution. “Spontaneous generation” has serious
problems. First, the same energy from sunlight, lightning, and volcanic
explosions that split up the compounds in the atmosphere would have even more
quickly destroyed any amino acids that formed. So, the amino acids had to reach
the oceans quickly for protection. However, science writer George Wald observes
that in the water “spontaneous dissolution is much more probable, and hence
proceeds more rapidly, than spontaneous synthesis.”19 Mike Riddle, a
creationist, explains that water immediately destroys amino
acids by hydrolysis (“water
splitting”). The entry of a water molecule between two bonded molecules (such
as amino acids) causes them to split. The “water tends to break chains of amino
acids apart. If any protein had formed in the oceans 3.5 billion years ago,
they would have quickly disintegrated.”20
“Catch 22” situation. If there was no oxygen in the
atmosphere, there would have been no ozone layer, and the ultraviolet rays from
the sun would have instantly destroyed any newly forming amino acids. If there
was oxygen, it would have soon oxidized and destroyed any self-organizing amino
acids. Either way, the emergence of life was doomed from the start. Author
Michael Denton notes in his book Evolution:
A Theory in Crisis (1985): “What we have is a sort of a ‘Catch 22’ situation.
If we have oxygen we have no organic compounds, but if we don’t have oxygen we
have none either”21 It was a no-win
situation. But then something, or Someone, intervened.
Biogenesis vs. Abiogenesis
In
the 1600s scientists believed life could arise from decaying matter, because
maggots and flies emerged from dung, rotting meat, and
garbage. Italian biologist Francesco Redi demonstrated in 1668
that maggots did not appear in meat if kept away from flies.22 In
1768 another Italian, naturalist Lazzaro Spallanzani, proved that substances
originally containing microorganisms, when boiled and then sealed, remained
microbe-free.23
It
did not keep German biologist Ernst Haeckel (1834-1919), a rabid Darwinian,
from promoting abiogenesis. Biochemist Michael Behe says: “From the limited
view of cells that microscopes provided, Haeckel believed that a cell was a
‘simple little lump of albuminous combination of carbon,’ not much different
from a piece of microscopic Jell-O. So it seemed to Haeckel that such simple life,
with no internal organs, could be produced from inanimate material.”24
Famous
French microbiologist Louis Pasteur refuted abiogenesis in 1862 in his “On the
Organized Particles Existing in the Air.” He showed that microbes would grow
only if a solution was exposed to air with spores of bacteria. In 1869, British
physicist John Tyndall demonstrated that when dust was present putrefaction
occurred; in the absence of dust, no decay took place.25
Lab-created “life”?
In
1953 chemist Stanley Miller, a graduate student at the
However,
the experiment used a manmade “atmosphere” that did not
include oxygen, which would have produced a different result. The process also had
“unnatural” components such as a “trap” (which quickly removed chemical
products from the destructive energy sources that made them). Further,
biologist Gary Parker notes: “The molecules Miller made did not include only
the amino acids required for living systems; they included even greater
quantities of amino acids that would be highly destructive to any ‘evolving’
life.”26
Besides,
half the amino acids produced were chemically “right-handed.” Every living protein, whether in animals, plants, molds, bacteria,
and even viruses -- except in some diseased or aging tissue –
is made up of at least 300 amino acids, practically all of them structurally
“left-handed.” Hence, the probability of a living protein being formed through
sheer chance is equal to unerringly getting 300 “heads” in a row from the toss
of a coin.
Co-authors
Sir Fred Hoyle and Chandra Wickramasinghe calculated the odds for a living
protein to form solely by chance in one place as just one chance in 1040,000.
In comparison, statisticians regard a probability of less than 1 in 1050
to be an absolute impossibility. They concluded that it was “an outrageously
small probability that could not be faced even if the whole universe consisted
of organic soup.”27
The
Miller-Urey experiment (and all other experiments after it) failed to produce
even one single living protein – never mind that a protein still has a long,
long way to go before becoming a complete living cell.
Enough time and chance?
Some
scientists argue that, given enough time, as well as chance, all things are
possible – even the emergence of the first living things from inanimate matter.
Writer C. Folsome asked them in the magazine Scientific American: “Can we really form a biological cell by
waiting for chance combinations of organic compounds? Harold Morowitz, in his
book Energy Flow and Biology,
computed that merely to create a bacterium would require more time than the
Universe might ever see if chance combinations of its molecules were the only
driving force.”28
Chemist
Ilya Prigogine, 1977 Nobel Prize laureate, sums it up in Physics Today: “The idea of the spontaneous genesis of life in its
present form is therefore improbable, even on the scale of billions of years.”29
Gerald Schroeder informs us that: “Since 1979, articles based on the premise
that life arose through chance random reactions over billions of years are not
accepted in reputable journals.”30
The “simple” cell.
Charles
Darwin believed that single-celled organisms were most primitive. Until the
first half of the 20th century, scientists called the most basic
living unit the “simple cell” -- made up of nothing more than a jelly-like
“protoplasm.”
In
1963 Dr. George Palade of the Rockefeller Institute discovered a complex
network of minuscule tubes and sacs within the protoplasm, now called the
“endoplasmic reticulum.”31 It became evident that
there is no such thing as a “simple” cell. Even the earliest unicellular
organisms on earth were unimaginably complex. Molecular biologist Jonathan
Wells and mathematician William Dembski concur that “the simplest life forms we
know, the prokaryotic cells (such as bacteria, which lack a nucleus), are
themselves immensely complex. Moreover, they are every bit as high-tech as the
eukaryotic cells…”32 Single-celled animals can “catch food, digest
it, get rid of wastes, move around, build houses, engage in sexual activity…
with no tissues, no organs, no hearts and no minds…”33 They even
communicate with each other using chemicals.
We read in the National
Geographic: “Each cell is a world brimming with as many as two hundred
trillion tiny groups of atoms called molecules.”34 Newsweek is quite graphic: “Each of
those 100 trillion cells functions like a walled city. Power plants generate
the cell’s energy. Factories produce proteins, vital units of chemical
commerce. Complex transportation systems guide specific chemicals from point to
point within the cell and beyond. Sentries at the barricades control the export
and import markets, and monitor the outside world for signs of danger.
Disciplined biological armies stand ready to grapple with invaders. A
centralized genetic government maintains order.”35
In addition, the “simple” cell has one capability not even
today’s most advanced machines can do: It can replicate its entire structure
within a matter of a few hours.
____________________
17.Richard Dawkins, The Selfish Gene, 1976, p. 16
18.ScienceDaily,
Mar. 22, 2006, Internet
19.George Wald, “The
Origin of Life,” Scientific American,
August 1954, pp. 49-50
20.Mike
Riddle, “Can Natural Processes Explain the Origin of Life?”, The New Answers Book 2, 2008, p. 66
21.Michael Denton, Evolution: A Theory in Crisis, 1985, p.
261
22.Spontaneous
Generation, World Book 2005
(Deluxe)
23.Spontaneous
Generation, Microsoft Encarta
Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
24.Michael Behe, Darwin’s Black Box: The Biochemical
Challenge to Evolution, 1996, pp. 23-24
25.Spontaneous
Generation, op. cit.
26.Gary Parker and
Henry Morris, What Is Creation Science,
1982, p. 40
27.Fred Hoyle and
Chandra Wickramasinghe, Evolution from
Space, 1981, p. 24
28.C. Folsome, “Life:
Origin and Evolution, Scientific American,
1979; quoted by Schroeder, op. cit., p.
89
29.I. Prigogine, et
al. , “Thermodynamics of Evolution,” Physics
Today, Nov. 1972, pp. 25:23, and Dec. 1972, pp. 25:38
30.Schroeder, op. cit., p. 89
31.Petersen,
op. cit., p.
92
32.Jonathan Wells and
William Dembski, How to Be an
Intellectually Fulfilled Atheist (or Not), 2008, p. 4
33.L.L. Larison
Cudmore, The Center of Life, 1977,
pp. 13-14
34.Rick Gore, “The
Awesome Worlds Within a Cell,” National
Geographic, September 1976, pp. 357-360
35.Peter Gwynne,
Sharon Begley and Mary Hager, “The Secrets of the Human Cell,” Newsweek, August 20, 1979, p. 48
(Excerpted from
Chapter 5, Early Earth Enigmas, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the
Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Early Earth Enigmas (Part 3)
The
theory of evolution
The
roots of the theory of evolution goes back many years before Charles Darwin. In
the 17th century, scientists like Francis Bacon and William Harvey
recognized it.
In
1855, Alfred Russel Wallace published the theory of evolution in a brief note
in the Annals and Magazine of Natural
History. On March 9, 1858, he explained the theory in a letter to Charles Darwin.37
Twenty months later, in 1859, Darwin published a more detailed version of the
theory in his book that he had been at work on earlier: On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the
Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. It became an
instant sensation.
The
Theory of Evolution posits that all living things changed through the ages into
all the life forms today. From the first living cell, “simple” organisms
evolved into fish, then into amphibians, then into reptiles, then into birds
and mammals, then into primates and, eventually, man.
“Ontogeny
recapitulates phylogeny”?
Ernst
Heinrich Haeckel helped spread
Haeckel,
however, cheated. He altered illustrations to fit his theory when the similarity
of embryos was not satisfactory. He was found out, charged with fraud, and convicted
by a university court at
Surprisingly,
many modern textbooks still include the disproved idea as proof for evolution.
Mutation: engine of evolution?
Evolutionists
claim that mutation, a change in the genetic material (DNA) inside the cells of
plants and animals, is the engine of evolution. Mutational changes are said to
be passed on to descendants – producing “improved” new members of the species,
which gradually turn into a new distinct species.
Harmful, not helpful. For mutation to happen, new information
has to be introduced in the genes of the organism. Yet, practically all
mutations showed a loss, rather than a gain, of genetic information – resulting
in missing eyes, limbs, wings, tails, etc. Author Lee Spetner (Not by Chance, 1996) reports: “All point mutations that have been studied on
the molecular level turn out to reduce the genetic information and not to
increase it.”40
In
any case, slight mutational changes are usually insignificant, but major
genetic mutations, instead of producing improved organisms, are generally harmful to the species.
Author Peo C. Koller (Chromosomes and
Genes, 1971) tells us: “The greatest proportion of mutations are
deleterious to the individual who carries the mutated gene. It was found in
experiments that, for every successful or useful mutation, there are many
thousands which are harmful.”41 The Encylopedia Americana says that “mutants illustrated in biology
textbooks are a collection of freaks and monstrosities, and mutation seems to
be a destructive rather than a constructive process.”42
Author
G. Ledyard Stebbins (Processes of Organic
Evolution, 1971) relates that in laboratory experiments, mutated insects
were kept with normal members of their species. “After a greater or lesser
number of generations the mutants are eliminated.”43 They were unable
to compete and died off, because they had become less adapted for survival than
their normal fellows.
Statistically improbable. Researchers often conduct experiments with
fruit flies, chosen for their short life spans. Gordon Rattray Taylor, former chief
science advisor of BBC TV (The Great
Evolution Mystery, 1983), observed: “It is a striking, but not much
mentioned fact that, though geneticists have been breeding fruit-flies for
sixty years or more in labs all round the world -- flies which produce a new
generation every eleven days -- they have never yet seen the emergence of a new
species or even a new enzyme.”44 Although fruit flies can be made to
mutate into deformed specimens, they are all still fruit flies.
Co-authors
P. Moorhead and M. Kaplan (“Mathematical Challenges to the Neo-Darwinian
Interpretation of Evolution,” 1967) report: “The Wistar Institute symposium in
1967 brought together leading biologists and mathematicians in what turned out
to be a futile attempt to find a mathematically reasonable basis for the
assumption that random mutations are the driving force behind evolution.
Unfortunately, each time the mathematics showed the statistical improbability
of a given assumption…”45
Pierre-Paul
Grasse, former
Anti-mutation mechanisms.
Two
British scientists, Dr. A.R. Fersht and Dr. G.R. Lambert, made an important
“discovery that enzymes exist within living cells that have just one assignment
in nature. They find and correct any errors in the genetic code. These errors
can creep into the code because of radiation, some chemicals, or for other
reasons. However, these enzymes faithfully correct any errors, preventing
mutations.”47 Francis Hitching (The
Neck of the Giraffe, 1982) adds: “Genes are a powerful stabilizing
mechanism whose main function is to prevent new forms evolving.”48
The
law of genetics dictates that the offspring of the parent organism shall be of
the same species. This is exactly what the Bible teaches: “But God giveth it a body as it hath pleased him, and to every seed his
own body. All flesh is not the same flesh: but there is one kind of flesh of
men, another flesh of beasts, another of fishes, and another of birds” (1
Cor
Microevolution vs.
macroevolution
Pierre-Paul Grasse, a zoologist,
observed that adaptations within species have nothing to do with evolution.
They are just minor changes around a stable genotype. For example, there are no
less than 200 breeds of dog today, descended from just a few ancient dogs and
wolves. They range from tiny
In
breeding experiments, scientists have tried to keep modifying selected plants
and animals indefinitely by crossbreeding to see if they could develop new
species. Result? “Breeders usually find that after a few generations, an
optimum is reached beyond which further improvement is impossible, and there
has been no new species formed… Breeding procedures, therefore, would seem to
refute, rather than support evolution.”49
Microevolution in reverse. In the 1930s brothers Heinz and Lutz
Heck, Munich Zoo and Berlin Zoo directors, respectively, recreated extinct
animals. First was the tarpan, a Stone Age horse whose drawings were on the
walls of caves in
They
had actually followed their father, who, while running the Berlin Zoo, crossed
the ibex (a wild goat) with domesticated goats. The older Heck produced animals
with the exact color of the bezoar, the Middle Eastern wild goat that was the
progenitor of all goats today.
The
Heck brothers also recreated the auroch, the ancestor of modern cattle. The
last of the huge auroch, which weighed up to a ton, died in a game preserve in
____________________
36Loren C. Eiseley, Darwin and the Mysterious Mr. X, 1979, pp. 45–80
37Wallace, Alfred Russell, Encyclopaedia Britannica 2009 Student and Home Edition
38Ashley Montagu, quoted by Luther D. Sunderland in Darwin’s Enigma, 1984, p. 119
39George Gaylord Simpson and William S. Beck, Life: An Introduction to Biology, 1965, p. 241
40Lee Spetner, Not by Chance, 1996, p. 138
41Peo C. Koller, Chromosomes and Genes, 1971, p. 127
42Encyclopedia Americana, 1977, Vol. 10, p. 742
43G. Ledyard Stebbins, Processes of Organic Evolution, 1971, pp. 24-25
44Gordon Rattray Taylor, The Great Evolution Mystery, 1983, p. 48
45P. Moorhead and M. Kaplan, “Mathematical Challenges to the Neo-Darwinian Interpretation of Evolution,” Proceedings of the Symposium, Wistar Institute of Biology, 1967; cited by Schroeder, op. cit. p. 119
46Pierre-Paul Grasse, Evolution of Living Organisms, 1977, pp. 88,103
47Martin Hunter, “There’s a Lot of Holes in Evolutionary Theory,” May 12, 1998, tract
48Francis Hitching, The Neck of the Giraffe, 1982, p. 103
49On Call, July 3, 1972, pp. 8,9
50“Turning Back Nature’s Clock,” Strange Stories, Amazing Facts, 1975, pp. 104-105
(Excerpted from
Chapter 5, Early Earth Enigmas, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the
Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Early Earth Enigmas (Part 4)
Problems with
evolution
There
were a few gaps in the “evolutionary tree” when
We
read in the Newsweek magazine issue
of
Evolutionary
gaps.
David B.
Kitts of the School of Geology and Geophysics, University of Oklahoma, said in
the September 1974 issue of the journal Evolution:
“Despite the bright promise that paleontology provides a means of ‘seeing’
evolution, it has presented some nasty difficulties for evolutionists the most
notorious of which is the presence of ‘gaps’ in the fossil record. Evolution
requires intermediate forms between species and paleontology does not provide
them.”52
Norman
D. Newell, former Curator of Historical Geology at the
In
No
transitional forms.
Many one-celled
life forms exist, but there are no known forms of life with 2, 3, 4, or 5
cells. Multi-celled organisms with 6–20 cells are parasites that depend on complex
animals as hosts to perform functions such as respiration and digestion for
them. If evolution is true, there should be transitional forms with 2–5 cells
even as fossils.
Plants. Some 375,000 species of plants
exist on earth today, and most have not changed from the way they first
appeared as fossils. Geneticist Jerry Bergman notes in the Technical Journal (Internet): “A major problem for Neo-Darwinism is
the complete lack of evidence for plant evolution in the fossil record. As a
whole, the fossil evidence of prehistoric plants is actually very good, yet no convincing
transitional forms have been discovered in the abundant fossil record.”54
If plants
evolved, nonvascular plants should have preceded vascular plants (with
sap-carrying channels). However, there are no fossilized nonvascular plants in
the rock layers formed before the earliest vascular plants appeared. Further,
no traces of stages leading to the development of seeds and fruits have been
found.
Arthropods. Of creatures with jointed legs,
the
Vertebrates. A backbone distinguishes the
fish, the first vertebrate, from invertebrates. For the fish to evolve into an
amphibian, it had to develop a pelvic bone for legs to be attached to; but no
fossil fish with an emergent pelvis has ever been found, not even the
coelacanth. The fish has a heart with two chambers, an amphibian heart has
three. The lungfish, which has gills plus a swim bladder it uses for breathing
out of water, is often said to be the link between fish and amphibians. But the
skull is entirely different. David Attenborough (Life on Earth, 1979) says that “the bones of their skulls are so
different from those of the first fossil amphibians that one cannot be derived
from the other.”57 Apparently, neither the lungfish nor the
coelacanth evolved into amphibians.
Richard
Milton (Shattering the Myths of Darwinism,
1997) notes: “Although each of these classes (fishes, amphibians, reptiles,
mammals, and primates) is well represented in the fossil record, as of yet no
one has discovered a fossil creature that is indisputably transitional between
one species and another species. Not a single undisputed ‘missing link’ has
been found in all the exposed rocks of the Earth’s crust despite the most careful
and extensive searches.”58
A “missing link”? Just a second. Have we not earlier
seen the archaeopteryx, which looks like the link between reptiles and birds?
Some scientists
believe birds evolved from theropods (dinosaurs that walked on hind legs). However,
theropods had tiny “arms,” compared to the large wings of early birds.
Moreover, their “hands” differed. Ann C. Burke and Alan Feduccia tell us in Science magazine (October 24, 1997): “Theropods
have ‘fingers’ I, II, and III (having lost the ‘ring finger’ and little
finger), while birds have fingers II, III, and IV.”59 In the same
issue, Richard Hinchliffe notes that “most theropod dinosaurs and in particular
the birdlike dromaeosaurs are all very much later in the fossil record than Archaeopteryx
(the supposed first bird).”60 In a subsequent issue (November 14, 1997),
John Ruben et. al. argue that “a transition from a crocodilian to a bird lung
would be impossible, because the transitional animal would have a
life-threatening hernia or hole in its diaphragm.”61
While
the archaeopteryx appears like half-reptile and half-bird, no fossil remains
look like an intermediate between a reptile and the archaeopteryx, or between
the archaeopteryx and a true bird. W.E. Swinton (“The Origin of Birds,” Biology and Comparative Physiology of Birds,
1960) concluded: “The origin of birds is largely a matter of deduction. There
is no fossil evidence of the stages through which the remarkable change from
reptile to bird was achieved.”62
Hybrids? There are other creatures that
look like crosses between species, but are not. Whales, porpoises, dolphins,
and manatees live in the water and look like fish, but they are mammals that
suckle their young. Of course, the most enigmatic hybrid-looking animal is the
platypus. It has a bill like a duck, feeds underwater like a fish, and lays
eggs like a bird or reptile, but is actually a mammal that produces milk for
its offspring. The only member of the Ornithorhynchidae (“bird-snout”) family,
the platypus has neither “evolutionary” ancestors nor descendants even vaguely
resembling it.
Charles
Darwin had agonized: “Why, if species have descended from other species by fine
gradations, do we not everywhere see innumerable transitional forms?... Why do
we not find them imbedded in countless numbers in the crust of the earth?63
And
why, if evolution is true, does it seem to have stopped?
Vestigial organs?
Several seemingly useless parts of the human body,
presumed to be evolutionary “leftovers,” are cited as proofs for the theory of
evolution. Are they? Here are some of the best known.
Appendix. It is most often mentioned by
evolutionists as one of the so-called “vestigial organs.” But it has been found
that the appendix is part of the lymphatic system, which, especially in early life,
produces antibodies that fight infections in the digestive system.64
Tonsils (adenoids). These used to be removed from children when inflamed, but are now
medically known to protect the nose and throat from
infection against invading bacteria and viruses. They also filter out
harmful substances that could pass into the digestive system. There are
indications that people who have had their tonsils removed experience more
problems in the upper respiratory tract.65
Thymus. An organ in the
chest cavity that shrinks from childhood until maturity, the thymus is now
recognized as the control center of the body’s defense system against germs.
Coccyx. Better known as the “tailbone,”
it supposedly shows man evolved from monkeys. However, patients who have had their
tailbones removed have difficulty sitting. The coccyx also holds the muscles
for bowel and childbirth movements, supports internal organs, and keeps the end
of the alimentary canal closed. It anchors the gluteus maximus, the large
muscle along the back of the thigh, which enables us to walk upright (something
monkeys cannot do).
Writers
Mario Seiglie et al. tell us in The Good
News magazine (November-December 2006): “The list of what were once
considered vestigial organs in our body has gone down from 100 in the early 20th
century to virtually zero…”66
____________________
51Enigmas of
Evolution,” Newsweek, March 29, 1982,
p. 39
52David B. Kitts,
“Paleontology and Evolutionary Theory,” Evolution,
September 1974, p. 467
53Norman D. Newell,
“The Nature of the Fossil Record,” Adventures
in Earth History, 1970, pp. 644–645
54“The Evolution of
Plants: A Major Problem for Darwinists,” Technical
Journal, 2002, Internet
55Quoted in “What About
Plant Evolution,” The Good News,
November-December 2009, p. 13
56Frank M. Carpenter,
“Fossil Insects,” Insects, 1952,
p. 18
57David Attenborough, Life on Earth, 1979, p. 137
58Richard Milton, Shattering the Myths of Darwinism, 1997,
pp. 253-254
59Ann C. Burke and Alan
Feduccia, “Developmental Patterns and the Identification of Homologies in the
Avian Hand,” Science, 24 October
1997, pp. 666–668
60Richard Hinchliffe,
“The Forward March of the Bird-Dinosaurs Halted?” Science, 24 October 1997, p. 597
61John A. Ruben et al.,
“Lung Structure and Ventilation in Theropod Dinosaurs and Early Birds, Science, pp. 1267–1270
62W. E. Swinton,
“The Origin of Birds,” Biology and
Comparative Physiology of Birds, 1960, p. 1
63Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species, Masterpieces
of Science edition, 1958, pp. 136-137
64David Menton, “The
Human Tail and Other Tales of Evolution,” St.
Louis MetroVoice, January 1994
65J.D. Ratcliff, Your Body and How It Works, 1974, p. 137
66Mario Seiglie, Tom
Robinson and Scott Ashley, “Evolution’s ‘vestigial organ’ argument debunked,”
God, Science and the Bible, The Good News,
November/December 2006, p. 11
(Excerpted from
Chapter 5, Early Earth Enigmas, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the
Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Early Earth Enigmas (Part 5)
“Irreducible
complexity.”
All
organisms, from cells to humans, are “irreducibly complex” – all their basic components
have to be in place before they can function. Thus, all species, extinct or
extant, appear fully developed. There is no known partially-developed species.
Evolution,
though, is believed to work through small, gradual steps, keeping new traits
that it finds functional. Will it keep in reserve anything that does not work,
even if potentially useful? There are no instances of half-developed appendages
or organs in any fossilized or living organism – no budding eyes that could not
see or partial wings that could not fly.
Blood clotting. Vital to healing wounds, blood-clotting
in animals and man involves 20–30 complex chemical steps. Omission of one step,
inclusion of an abnormal step, or alteration of the timing of a step will
prevent blood from clotting and lead to death. If the first few of the many
blood clotting factors were not immediately useful, the body would not have
kept them, unaware that the rest of the factors would also form. How did such a
complex, yet precise, process fully develop?
Charles
Darwin had confessed in his famous book: “If it could be demonstrated that any
complex organ existed which could not possibly have been formed by numerous,
successive, slight modifications, my theory would absolutely break down.”67
The eye. As a human embryo develops in its
mother’s womb, some one million optic nerves start to grow from the back of
each eye, simultaneous with a corresponding one million nerves from the brain.
Each of the millions of nerves from both sides has to make its way through the
tissues in between and connect to its counterpart – much like two work teams digging
a tunnel from opposite sides of a mountain must meet precisely at the center
according to the engineer’s plan.
Most
animals, invertebrates as well as vertebrates, have eyes. Even the sea wasp, a
jellyfish, has eyes. Among of the strangest are multiple-lensed, compound eyes
found in fossilized worms!68
Did
the eye evolve?
Solomon
understood the matter quite well. “The
hearing ear, and the seeing eye, the LORD hath made even both of them” (Prov
In
the sixth edition of his book, Darwin junked the idea of natural selection or
“survival of the fittest” as the driving force behind the theory of evolution:
“Natural selection is incompetent to account for the incipient stages of useful
structures,” he said.70
Genetic
pre-programming.
How
does evolution explain metamorphosis -- the form-changing stages in the life
cycles of insects, amphibians, and crustaceans? Most of them hatch from eggs as
larvae. Were they once all larvae before they evolved into more advanced forms?
One may say larvae, just like some worms, reproduced sexually in the distant
past. But there is no trace of reproductive organs in any type of larva. And,
if a larva could not reproduce, how could it have evolved?
Some
insect larvae pass through a cocoon stage when their brains, nerves, muscles,
eyes, and other organs dissolve into goo. Does it mean some larvae evolved into
goo before becoming, say, butterflies? How did they survive as goo for
thousands or even millions of years?
Metamorphosis
exemplifies genetic pre-programming. Similarly, ants and termites have the
ability to grow wings in order to migrate when their colonies become
overpopulated or destroyed. The insects use their wings for just one short
flight, before shedding them to seek mates.71 Obviously, these are
not cases of biological evolution.
The Cambrian “explosion.”
For
nearly 3 billion years since life first appeared on earth, organisms remained
microscopic in size: bacteria, protozoan, Ediacaran spheres and discs without
mouths and appendages.72 Then, suddenly: the Cambrian “explosion.” Time magazine’s cover story in its
All anatomical designs. In a quantum leap, life advanced from
microbial, amorphous organisms to complex multi-cellular life forms: rotifers,
annelids (worms), arthropods, fish – equipped with jointed, food-gathering
appendages, intestines, notochords, gills, eyes – all the anatomical designs
found in the animal phyla existing today. Oddly, no new phylum has appeared
since the Cambrian Explosion. Succeeding developments
have been confined to variations within each phylum.74
In
fact, says Paul Chien, Biology Dept. Chair of the
He
adds: “Also, the animal explosion caught people’s
attention when the Chinese confirmed they found a genus now called Yunnanzoon
that was present in the very beginning. This genus is considered a chordate,
and the phylum Chordata includes fish, mammals and man. An evolutionist would
say the ancestor of humans was present then. Looked at more objectively, you
could say the most complex animal group, the chordates, were represented at the
beginning, and they did not go through a slow gradual evolution to become a
chordate.”76
No ancestors. For new life forms to appear, it would
have taken hundreds of millions of years for the thousands of mutations needed
to alter existing genes. Yet, the fossil record indicates that the Cambrian
Explosion transpired in 5 million years or less.77 Further, there is
no evidence of mutational evolution within the 5-million-year span of the
Cambrian explosion.78,79 Colin Patterson (Evolution, 1978) avers: "Most of the major groups of animals
(phyla) appear fully fledged in the early Cambrian rocks and we know of no
fossil forms linking them."80
Paleontologist
Alfred S. Romer corroborates that: “Below this (Cambrian period), there are
vast thicknesses of sediments in which the progenitors of the Cambrian forms
would be expected. But we do not find them; these older beds are almost barren
of evidence of life, and the general picture could reasonably be said to be
consistent with the idea of a special creation at the beginning of Cambrian
times.”81
Surprisingly,
even staunch evolutionist Richard Dawkins seems to agree: “If progressive
evolution, from simple to complex is correct, the ancestors of these full-blown
creatures in the Cambrian should be found; but they have not been found and
scientists admit there is little prospect of their ever being found. On the
basis of the facts alone, on the basis of what is actually found in the earth,
the theory of a sudden creative act in which the major forms of life were
established fits best.”82
Sudden entry and exit. Many scientists have arrived at that
conclusion. David M. Raup (Field Museum
of Natural History Bulletin, January 1979): “Species appear in the sequence
very suddenly, show little or no change during their existence in the record,
then abruptly go out of the record.”84 Steven M. Stanley (The New Evolutionary Timetable, 1981):
“The record now reveals that species typically survive for a hundred thousand
generations, or even a million or more, without evolving very much… After their
origins, most species undergo little evolution before becoming extinct.”85
George
Sim Johnston (“An Evening with
Unscientific
theory.
C.F.
Morgan (“Evolution Not Based on Fact,” 1998) points out that “true science is
limited to observable phenomena. To be truly scientific, something must be
observable, documentable, repeatable, experimentally verifiable, and testable,
among other things. Conversely, evolution is a philosophical belief about the
past based upon subjective interpretations and opinions of scientific data
which exists in the present… Evolution is not a fact. It is not even a good
theory. It has never been observed, and there is no direct evidence that it has
ever occurred. It is no more than a religious or philosophical belief based
upon choice, not science.”89
Mathematician I.L. Cohen (Darwin Was Wrong: A Study in Probabilities, 1984) confirms that
“every single concept advanced by the theory of evolution (and amended
thereafter) is imaginary as it is not supported by the scientifically
established facts of microbiology, fossils, and mathematical probability
concepts.
Arthur
L. Bruce (“Evolution Is a Creation Myth,” 1998) comments: “Actually, evolution
is not even a scientific theory because it cannot be tested by the scientific
method. It is an unscientific hypothesis or speculation about origins that
contradicts the basic laws and facts of science. It is the ‘creation myth’ upon
which the religion of secular humanism is founded. Its proper place for study
in the public schools is not the science classroom but the social studies or
humanities classroom where it should be examined in comparison with the
classical myths and other religions of the world.”91 (In the late
1990s the states of
Austin
H. Clark (“Animal Evolution,” Quarterly
Review of Biology, December 1928) concedes: “Thus so far as concerns the
major groups of animals, the creationists seem to have the better of the
argument. There is not the slightest evidence that any one of the major groups
arose from any other. Each is a special animal complex related, more or less
closely, to all the rest, and appearing, therefore, as a special and distinct
creation.”92
Sir
Fred Hoyle and N. Chandra Wickramasinghe (Evolution
from Space: A Theory of Cosmic Creationism, 1981) conclude: “The speculations of The
Origin of Species turned out to be wrong… It is ironic that the scientific
facts throw
____________________
67Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species, 1859, p. 179
68Donald G. Mikulic et al., “A Silurian Soft-Bodied Biota,” Science, 10 May 1985, pp. 715–717
69Darwin, op. cit., pp. 146,175
70Op. cit., Sixth Edition, The Modern Library, 1872, p. 66
71Termite, World Book 2005 (Deluxe)
72Schroeder, op. cit. p. 94
73Madeline Nash, “When Life Exploded,” Time, Dec. 4, 1995, p. 68
74Schroeder, op. cit. pp. 92-93
75Paul Chien, “Explosion of Life,” 30 June 1997 Interview, origins.org/articles/chien_explosionoflife.html, p. 2
76Op. cit., p. 3
77S. Bowring et al., “Calibrating Rates of Early Cambrian Evolution,” Science, 1993; cited by Schroeder, op. cit., pp. 116-117
78R. Gore, “The Cambrian Explosion of Life,” National Geographic, October 1993
79R. Kerr, “Evolution’s Big Bang Gets Even More Explosive,” Science, 1993
80Colin Patterson, Evolution, 1978, p. 133
81Alfred S. Romer, “Darwin and the Fossil Record,” Natural History, October 1959, p. 466
82Richard Dawkins, The Selfish Gene, 1976, p. 14
83Charles Darwin, op. cit., 1902 edition, Part Two, p. 54
84David M. Raup, “Conflicts Between Darwin and Paleontology,” Field Museum of Natural History Bulletin, January 1979, p. 23
85Steven M. Stanley, The New Evolutionary Timetable, 1981, p. xv
86Stephen J. Gould, “Evolution’s Erratic Pace,” Natural History, May 1977, pp. 13-14
87George Sim Johnston, “An Evening with Darwin in New York,” Crisis, April 2006, Internet
88Adrian Desmond and J. Moore, Darwin: The Life of a Tormented Evolutionist, 1991, pp. 475-477
89C.F. (Frank) Morgan, “Evolution Not Based on Fact,” May 4, 1998, “Letters to the Editor,” National Institute for Inventors tract
90I.L. Cohen, Darwin Was Wrong: A Study in Probabilities, 1984, p. 209-210
91Arthur L. Bruce, “Evolution Is a Creation Myth,” May 23, 1998, “Letters to the Editor,” National Institute for Inventors tract
92Austin H. Clark, “Animal Evolution,” Quarterly Review of Biology, December 1928, p. 539
93Fred Hoyle and N. Chandra Wickramasinghe, Evolution from Space: A Theory of Cosmic Creationism, 1981, pp. 96–97
Early Earth Enigmas (Part 6)
Divinely designed DNA?
When the cell of a bacterium divides, it becomes two bacteria, not two amoebae. Apple trees bear apples, not oranges. A smooth-coated Siamese cat cannot give birth to thick-furred Persian kittens, although they belong to the same feline family. All living species, as well as varieties within them, stay the same from one generation to the next.
The Creator had apparently intended it to be that way from the very beginning: “And God said, Let the earth bring forth the living creature after his kind, cattle, and creeping thing, and beast of the earth after his kind: and it was so” (Gen
Physically responsible for this biological order is a chemical molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which forms part of threadlike chromosomes inside all living cells (except red blood cells and some viruses). In the form of two intertwined chains in a double helix (spiral), like a twisted ladder, each DNA comprises thousands of encoded genes that govern heredity, the transmission of physical characteristics from parent to offspring.
Proteins depend on DNA for their formation. Yet, DNA cannot form without pre-existing protein. Which came first?
Chemistry lecturer John C. Walton further lamented: “The origin of the genetic code presents formidable unsolved problems. The coded information in the nucleotide sequence is meaningless without the translation machinery, but the specification for this machinery is itself coded in the DNA. Thus without the machinery the information is meaningless, but without the coded information the machinery cannot be produced! This presents a paradox of the ‘chicken and egg’ variety, and attempts to solve it have so far been sterile.”94
Stored genetic information.
DNA is stored information written in a genetic language with a four-letter (nucleotide) alphabet and grammatical rules, telling the cells how to function and reproduce. Despite having only four letters, through their various combinations DNA is able to maintain the distinctions not only among all species, but also between individuals of each species. The language components in the human gene are identical to that of other organisms, say, a snail. Only the sequence is different.95
One of the tiniest one-celled organisms is the bacterium R. coli. Scientists estimate it has about 2,000 genes, with some 1,000 enzymes each. Every enzyme contains roughly one billion nucleotides or letters of the chemical alphabet, comparable to bytes in computer language.
Physicist Jonathan Sarfati reckons that the “amount of information that could be stored in a pinhead’s volume of DNA is equivalent to a pile of paperback books 500 times as high as the distance from Earth to the moon, each with a different, yet specific content. Putting it another way, while we think that our new 40 gigabyte hard drives are advanced technology, a pinhead of DNA could hold 100 million times more information.”96
Information from intelligence.
Information is nonmaterial and, therefore, could not have originated from matter. Information can only come from intelligence. Co-authors L. Lester and R. Bohlin tell us: “Intelligence is a necessity in the origin of any informational code, including the genetic code…”97 The vast amounts of information in the DNA can only have come from an intelligent source.
1962 Nobel Prize winner Francis Crick, co-discoverer of the DNA structure, had said that the more he studied the DNA double-helix, the more he became convinced that it could not have evolved by chance. In his book Life Itself, he wrote: “An honest man, armed with all the knowledge available to us now, could only state that, in some sense, the origins of life appears at the moment to be almost a miracle.”98
On
Designed on purpose. Biochemist Michael Behe of
Natural processes, such as mutation, cannot alter the DNA. I.L. Cohen says that “any physical change of any size, shape or form is strictly the result of purposeful alignment of billions of nucleotides (in the DNA). Nature or species do not have the capacity to rearrange them nor to add to them… The only way we know for a DNA to be altered is through a meaningful intervention from an outside source of intelligence – one who knows what it is doing, such as our genetic engineers are now performing in the laboratories…”101
Every living cell (except a few highly specialized ones) carries in its DNA all the information needed reproduce a new, identical organism. To clone an entire human being, the scientist needs just one cell.
____________________
94John C. Walton, “Organization and the Origin of Life,” Origins, 1977, pp. 30–31
95Dawkins, op. cit.,
96Jonathan Sarfati, DNA: Marvelous Messages or Mostly Mess?, March 2003, Internet
97L. Lester and R. Bohlin, The Natural Limits to Biological Change, 1989, p. 157
98Francis Crick, Life Itself, p. 88; quoted by Gary Stearman, “Rael, Inc., “Cloning for Life,” Prophecy in the News, February 2003, p. 12
99Jan Marcussen, Newsletter, Mid-January Y2K+11, p. 2
100Michael Behe, Darwin’s Black Box: The Biochemical Challenge to Evolution, 1996, p. 193
101Cohen, loc. cit.
(Excerpted from Chapter 5, Early Earth Enigmas, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)
Early Earth Enigmas (Part 7)
Alternative theories
The absence in the fossil record of transitional forms that would prove the Theory of Evolution has led many frustrated evolutionists to consider alternative theories for the development of life forms on Earth.
Theistic Evolution.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many Catholics and Protestants accepted Theistic Evolution, the belief that the process of biological evolution was divinely supervised. Theistic evolutionists believe that God created the first cell, then afterward allowed evolution to proceed, intervening only occasionally. He waited for primitive man to evolve into the first perfect human being before endowing him with a soul. The hybrid doctrine is a combination of divine creation and Darwinian evolution.
Botanist Asa Gray (d. 1888), one of
Geologist Arnold Guyot, a staunch anti-Darwinist, advocated at least three interventions by the Creator: first, when He created matter; second, when He created life; and, third, when He created man.102
Punctuated Equilibrium.
In an attempt to explain the absence of transitional forms, Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge, American Museum of Natural History curator, jointly proposed the theory of Punctuated Equilibrium in several articles in scientific publications (Mammals in Paleontology, 1972; Nature, 1993; Paleontology, 2007).103,104,105 Newsweek magazine reported on March 29, 1982: “In 1972 Gould and Niles Eldredge collaborated on a paper intended… to resolve a professional embarrassment for paleontologists: their inability to find the fossils of transitional forms between species, the so-called ‘missing links’.” Their concept: “Instead of changing gradually as one generation shades into the next, evolution as Gould sees it, proceeds in discrete leaps. According to the theory of punctuated equilibrium there are no transitional forms between species, and thus no missing links!”106
Gould and Eldredge speculate that speciation (the change from an old species to a new one) usually occurs in small, isolated, peripheral groups rather than in the main populations of species, making their fossilized remains harder to find. Fossils of the general population are usually found, which creates the impression of the unchanging nature or stasis of most species over millions of years.107
Panspermia (spores from space).
Sir Fred Hoyle mused that “life could not have originated here on the Earth. Nor does it look as though biological evolution can be explained from within an earth-bound theory of life.”108 Earlier, in 1908, Svante Arrhenius theorized that spores could have drifted to Earth from other star systems. These gave rise to the first living cells that later evolved into more complex organisms.109
Nobel laureate Francis Crick similarly proposed that “life on earth may have sprung from tiny organisms from a distant planet, sent here by space ship as part of a deliberate act of seeding”110 Crick gave the old theory, known as “panspermia” (from Greek pan, “of all,” and sperma, “seed”), a new twist: “directed panspermia.” Some people find this plausible. J. Horgan wrote in the Scientific American (February 1992): “Given the weaknesses of all theories of terrestrial genesis (the origin of life on Earth), directed panspermia (the deliberate planting of life on Earth) should still be considered a serious possibility.”111
Panspermia, though, fails to answer the question of life’s origin. It merely takes the problem of creation out to space. Just how life arose on a planet many light years away is not explained.
Progressive Creation
In the 1930s Russell L. Mixter, a Wheaton College graduate, formed the concept that God created the universe and the various forms of life on earth gradually, over millions and billions of years. Creation was accomplished in progressive steps -- hence the name of the doctrine: Progressive Creationism. In 1954 theologian Bernard Ramm wrote The Christian View of Science and Scripture, popularizing the idea which no longer demanded a young Earth and the recent creation of man.112
Progressive Creationism is thus a form of Old Earth creationism, accepting geological and cosmological estimates for the age of the Earth and the universe, while teaching that the successive species of plants and animals in the fossil record were the products of divine creation, not Darwinian evolution. As earlier organisms died off and became extinct, God created new species to replace them.
Most of God’s replacements were typically improved models. Each time, the basic forms or "templates" of previously existing life are used -- with just a few minor adjustments. For instance, the DNA of a gorilla has been found to be 97.8% similar to a man’s; the chimpanzee’s DNA resembles that of a human being by 98.2%.
The leading proponents of Progressive Creationism are Reasons To Believe, organized by astronomer Hugh Ross, and Answers in Creation, another organization set up in 2003 to publish rebuttals to Young Earth Creationists’ scientific claims, which are regarded as pseudoscience.113
____________________
102Theistic Evolution, Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
103“Punctuated Equilibria: An Alternative to Phyletic Gradualism,” Mammals in Paleontology, 1972, pp. 82-115
104“Punctuated Equilibrium Comes of Age,” Nature 366, 1993, pp. 223-227
105“Punctuated Equilibria: The Tempo and Mode of Evolution Reconsidered,” Paleontology, 2007, pp. 115-151
106Enigmas of Evolution,” Newsweek, March 29, 1982, p. 39
107Evolution, Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia Deluxe 2004
108Fred Hoyle, The Intelligent Universe, 1983, p. 242
109Cited by Gary Stearman, “Rael, Inc., “Cloning for Life,” Prophecy in the News, February 2003, p. 11
110Francis Crick, “Life Itself – Its Origin and Nature,” Futura, 1982; quoted by Mark Eastman and Chuck Missler, The Creator Beyond Time and Space, 1996, p. 62
111J. Horgan, “Profile: Francis H.C. Crick,” Scientific American, February 1992; quoted by Schroeder, op. cit., p. 90
112Old Earth Creationism, Wikipedia, Internet
113Progressive Creationism, Wikipedia, Internet
(Excerpted from Chapter 5, Early Earth Enigmas, THE DEEP THINGS OF GOD: A Primer on the Secrets of Heaven and Earth by M.M. Tauson, Amazon.com)